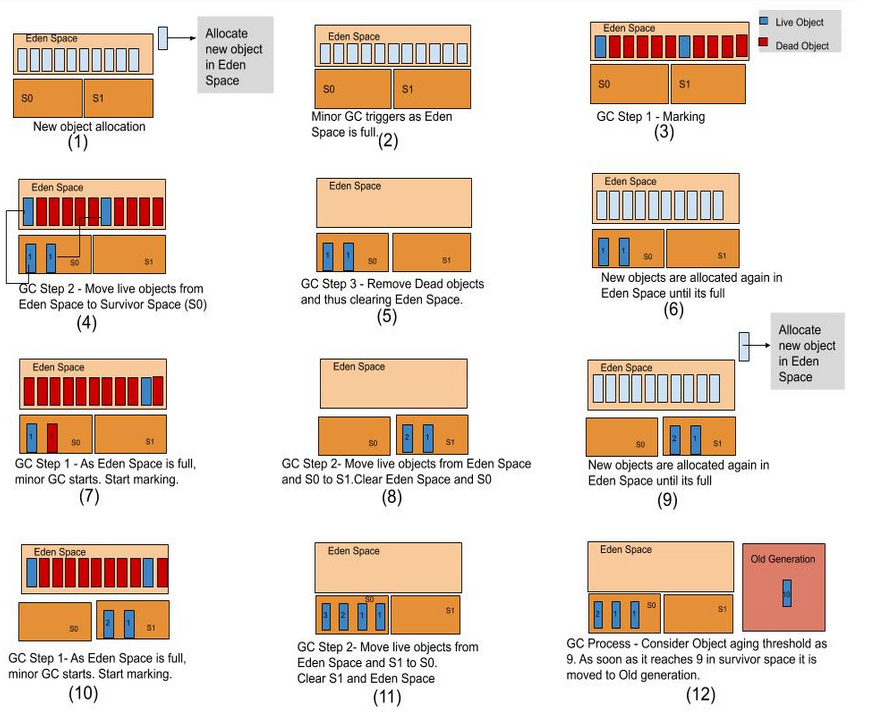
When was the last time you pulled out your wallet to make a cash payment? It’s probably been a while, isn’t it? While debit and credit cards continue to be the preferred mode of payment – digital transactions, bank transfers, and e-wallets are getting equally popular. Convenience and security are two important reasons why cashless transactions are preferred.
According to a 2018 survey conducted by payment processor TSYS (as seen on creditcards.com) that involved 1,222 consumers, 54% of the participants preferred paying via debit cards, 26% preferred credit cards, and only 14% expressed a preference for using cash. What’s interesting is that when compared to 2017’s report, the preference for payment by debit cards increased by 10%, indicating a continuous shift to cashless transactions.
Another survey by the Diary of Consumer Payment Choice (DCPC) suggests that the average amount of cash carried by consumers daily was $59, indicating that when consumers choose to pay in cash it is often when the amount is very small. The same report highlights that 55% of payments were made in cash but only when the net payment amount was under $10. The below image depicts the average cash holding by age group across the years:
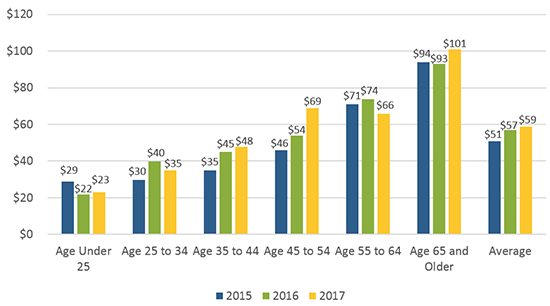
Image source
Types of digital payments:
- Device-centric mobile proximity wallet
It is a wallet that stores the user’s payment credentials in the mobile device. These credentials, at the point of purchase NFC (Near Field Communications) or MST (Magnetic Secure Transmission), are leveraged to enable proximity payments.
- Device-centric mobile in-app wallet
This wallet is used for in-app purchases where a debit/credit card isn’t available. This wallet uses the EMV payment token and the issuer’s identification and verification to complete the in-app purchase.
- Card-not-present or card-on-file wallet
A digital wallet that uses the previously-stored payment credentials of users. The term Card-on-File is referred to the authorized storage of the user’s payment credentials by a merchant.
- QR code wallet
Similar to CNP wallets these wallets are device agnostic and cloud-based. QR codes are used to complete the transaction at the POS. Paytm is an example of such wallets.
- Digital checkout wallet
The payment networks offer digital checkout wallets or digital acceptance services to both issuers and merchants. The networks support a web browser, mobile app, and in-app channels.
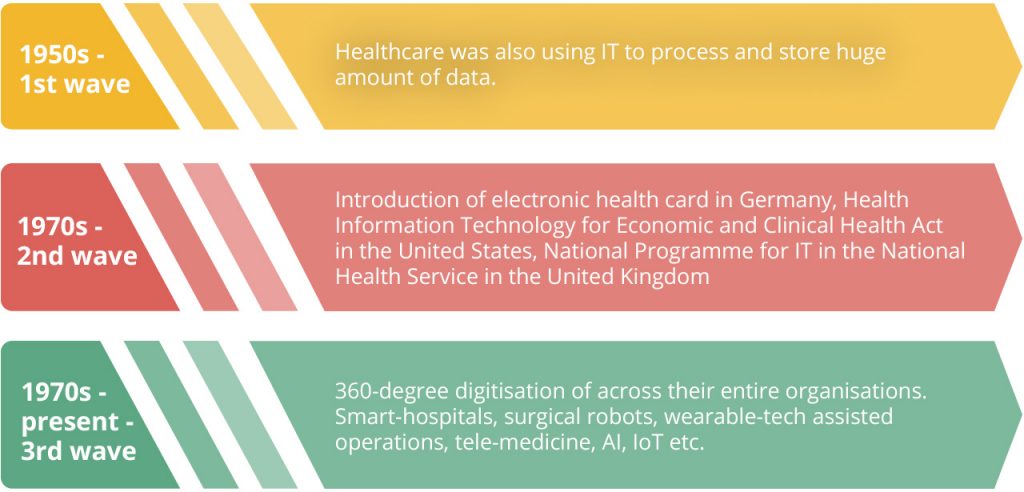
Evolution of digital payments and digital wallets
The early 90s
The digital wallet space has been in existence since the ’90s. Online payment services started to operate in the early 90s.
- Around this time PayPal was used as a software solution for eBay. However, the concept of storing payment information with an online provider to enable purchases outside of eBay initially didn’t catch up.
- Almost at the same time, more players emerged in the digital wallet industry. Some of the popular entities of that time were Millicent (founded in 1995), Ecash and CyberCoin (founded in 1996).
The Late 90s–2000s
Most of the earlier digital wallets were stored on the desktops of personal computers. By the early 2000s, the new-age digital wallets emerged which were compatible with wireless and other mobile devices, and were more often stored on a central server owned by a digital wallet vendor or Internet service provider (ISP).
The major drawback of such wallets during this time was the compatibility. Moreover, the dearth of one multipurpose wallet required customers to download various digital wallets from multiple vendors. It was thereby a complicated option for customers.
To deal with this drawback several financial and technology enterprises like MasterCard, Visa, American Express, IBM, Microsoft, Trintech, and CyberCash came together and established a digital wallet standard. They defined Electronic Commerce Modeling Language (ECML) as a standard mechanism to explicitly define a format for online order forms that could incorporate digital wallet technology from any vendor.
Launch of Apple Pay
A significant shift in the digital wallet landscape was witnessed only in 2014 with the launch of Apple Pay; the wallet was supported by over 220,000 merchant locations in the United States. Other giants like Google and Samsung soon followed with their payment options – Android Pay and Samsung Pay respectively.
2015-2019
According to a BCG report, 2015-16 was known to be a watershed period in the payment history, and the trend continues. Within a span of just 2 years, between 2015 – 2017, the total value of the mobile wallets market doubled.
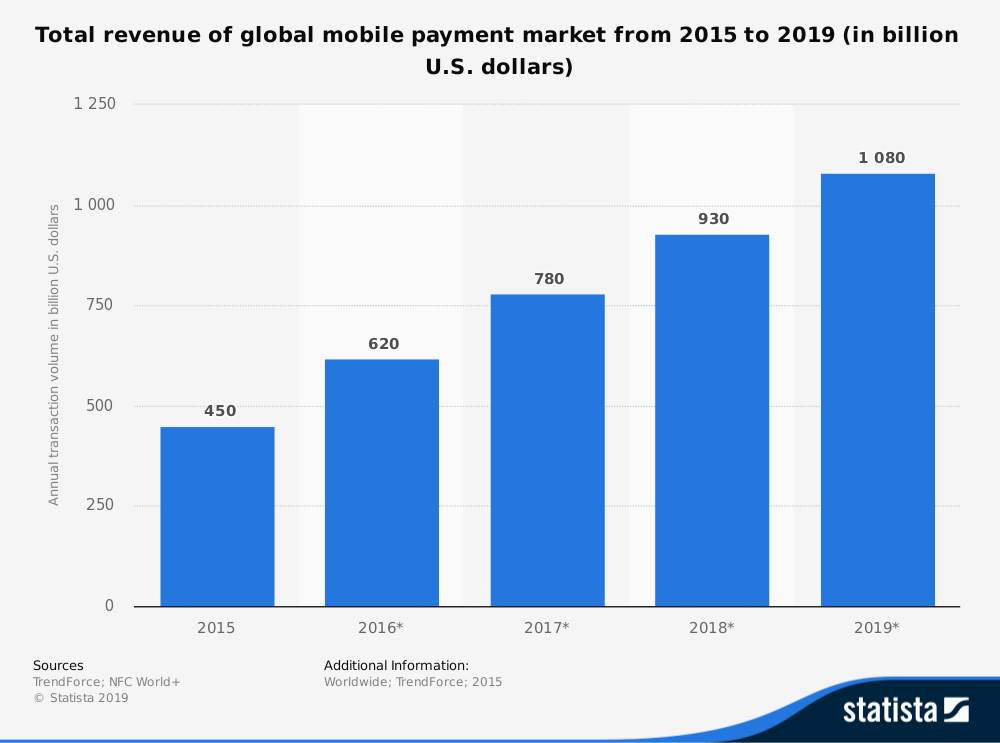
Image source
A 2018 Trends Report on Consumer Mobility released by Bank of America shows that P2P mobile payments, which is one to one payments over mobile wallets, increased from 36% in 2017 to 44% in 2018. An interesting fact here is that the number of mobile transaction users is rapidly increasing among the younger generation (51% of millennials said they used mobile wallets in 2018) while not so rapidly with people over the age group of 65, which stunted the overall increase in percentage but proved the shift to cashless transactions nonetheless.
Finally, late 2018 and 2019 saw a rapid rise in mobile wallets and digital transactions. This largely occurred due to the growth in technology that led to numerous e-payment vendors and apps. The added assurance of security through OTPs and passwords is fueling the transition from cash and card payments to mobile payments.
An eMarketer report released in December 2018 projected that almost 938 million people worldwide will make a payment over their smartphone in 2019. This number represents nearly 36% of all smartphone users and is an increase of 13.5% over 2018.
As per a survey by the Boston Consulting Group, the amount spent via digital wallets is expected to rise to $500-$550 billion by 2025.
Change leading the digital payments revolution:
There are four major shifts in the global technology landscape that have led to the digital wallet revolution:
- The ongoing digital revolution
- The entry of non-traditional players
- Evolution of a more demanding digitally-savvy consumer
- The emergence of new markets
The ongoing digital revolution
By 2020 it is expected that almost 75% of the world’s population will have access to the internet. 80% of these users will be accessing the internet through their mobile. Over the years, smartphones have gotten smarter and are equipped with high-end technologies like powerful processors, substantial memory, high-resolution cameras, barcode scanning, GPS geocoding, NFC-based technologies, social media platforms, etc. With all these armors, every smartphone user is a potential commerce enabler.
The evolution of smartphones is enabling new payment capabilities. This has revolutionized digital payments coupled with innovations in payment access and security technologies such as tokenization of card details for reducing fraud, biometric-enabled multi-factor authentication, EMV standards for user authentication, NFC-capable readers at merchant stores, hardware-based secure element approaches, etc.
The entry of non-traditional players
The digital wallet industry is not limited to Fintech and Financial enterprises. Over the years we have seen players across multiple industries entering the sector. These categories range from device manufacturers (Apple, Samsung, Google), technology and e-commerce enterprises (eBay, Alibaba, Amazon), telecom companies (Vodafone, Orange, Airtel) and start-ups like PayTM and FreeCharge in India, Google Pay, etc.
The disruption in the digital wallet space is further expected to heighten as the number of Fintech startups continues to grow. In the past five years, the number of such start-ups has doubled, with funding growing six times. The largest share of the overall Fintech funding, in fact, has gone to the payment Fintechs, spanning from wallets to integrated POS systems, P2P payments, and cross-border transfers, etc.
Some startups such as Ant Financial Services Group (China), First Data, Stripe and Mozido (USA) and One97 Communications (India), have grown to over USD 1 billion in valuation.
Evolution of a more demanding digitally-savvy consumer.
The tech-savvy consumer today has shifted to the digital platform for a lot of reasons, and hassle-free money transactions are one of them. The emergence of non-banking tech players along with retailers and e-commerce enterprises and the advent of features such as biometric authentication from ApplePay and integrated rewards from Starbucks, have to meet the customer’s expectations changing from payments solutions.
The consumer today expects a seamless digital experience from every interaction they have with brands in the virtual world. Hence, there is a growing need for an intuitive and frictionless user interface and design.
The digital wallets are expected to offer a seamless interaction on smartphones and apps to deliver on par with the evolving customer needs, both enhancing and increasing customer interactions and building relationships.
The emergence of new markets
According to a recent study, consumers in markets like India, South Korea, and China are more open to experimenting with mobile payments than the US, UK, Australia, and others. One of the reasons for this shift is the growing number of internet users in these countries.
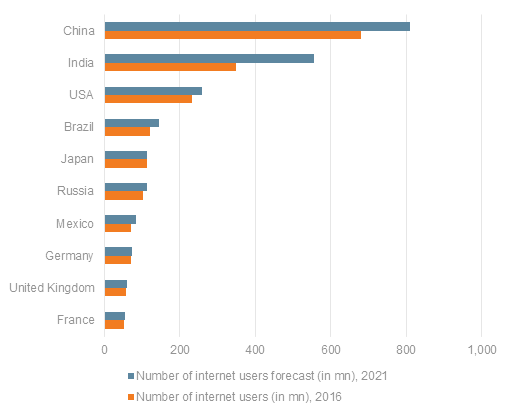
Image source
A DCR Strategies report revealed that by 2020, every 1 in 2 dollars spent online will come from a purchase made by a mobile phone. The same report also revealed that the global mobile wallet spends increased by 32% in 2017 to $1.35 trillion. Here are some interesting facts from the report : more than 50% of smartphone users don’t prefer carrying any payment instrument (cash or card) with them, one in three Canadians already paid for something through their mobile phone, and two thirds of Canadians are looking to stop using cheques and other outdated modes of payment.
The growth story of digital payments in India
The Indian economy has traditionally been dominated by cash. However, the increased adoption of smartphones together with a favorable regulatory environment is pushing the economy to a less cash-dependent state and promoting the usage of digital payments.
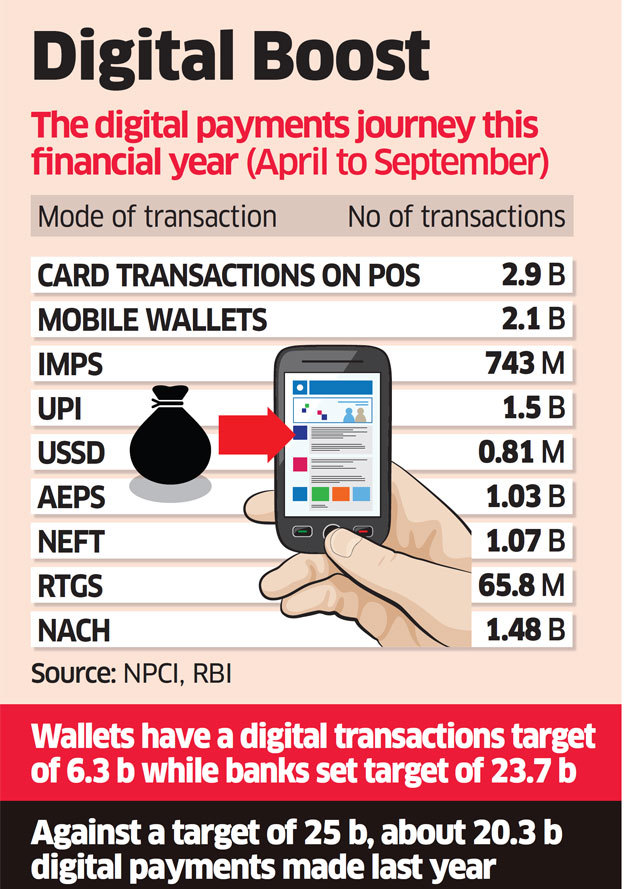
Image source
This report by Statista shows the rise in transactions on mobile phones in the past few years:
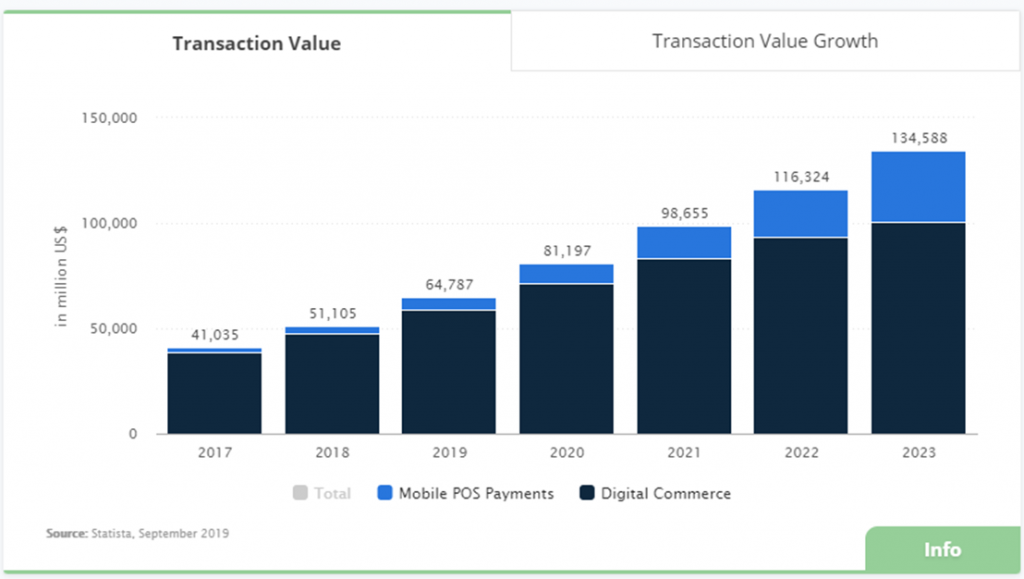
Image source
The parliament released a statement in July stating that the overall digital transactions in India increased by 51% to reach INR 3,133.58 Crore in 2018-2019.
According to a study by Assocham-PWC India, digital payments in India will increase from $64.8 billion to $135.2 billion in 2023, which is more than a 100% increase. The study stated that India is expected to clock ‘the fastest growth in digital payments’ between 2019 and 2023 with a CAG of over 20.2%. It also stated that on a worldwide transaction scale, India’s share in digital payments will increase from 1.56% to 2.02% between 2019 and 2023.
To further emphasize the move from cash to cashless transactions, a report by economic times India stated that debit and credit card transactions until September stood at 2.9 billion, mobile wallet transactions at 2.1 billion, and UPI at 1.5 billion.
The major contributors to this estimate will be the person to merchant (P2M) transactions driven by digital payments at the physical point of sale, followed by business to business (B2B) and peer to peer (P2P) transactions.
Digital wallets gained a major boost during the demonetization drive of 2016. Further, some key actions like – expansion of the digital payments infrastructure at merchant establishments, expansion into rural areas, relaxation in the PPI norms, incentivization of digital payments at fuel pumps, toll plazas, insurance portals, etc. and launch of the Bharat QR codes, have helped further in the adoption of technology.
The fastest-growing segment of digital payments is Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs), which has grown at a CAGR of 97% in the same period that now accounts for 10% of the total digital payments volume.
Mobile-wallet is the largest category within PPIs, but the segment also includes prepaid cards (including gift cards) as well as other paper vouchers.
Paytm leading the way to a cashless economy in India
Paytm is India’s largest mobile commerce platform. It started by offering mobile recharge and utility bill payments and today it offers a full marketplace to consumers on its mobile apps.
PayTM’s total annualized gross transaction value (GTV) grew four-fold to cross $20 billion in February 2018, as compared to 2017 and hit $50 billion GTV in FY19.
As of July 2019, PayTM has over 450 million registered customers with over 130 million of these as active users and over 12 million registered merchants. They are investing heavily to reach a target of 250 million monthly active users by March 2020.
Emerging markets to lead the way
Today’s consumers prefer faster and convenient solutions in all walks of life. As the world moves towards becoming cashless, initiatives taken by enterprises and governments to promote cashless societies, technological innovation, and financial inclusion will emerge as the key drivers of the significant growth rates of the non-cash transactions in the emerging markets.
While the proliferation of mobile payments and digital innovation are expected to be the levers of high growth across all the regions, differences in adoption patterns and development of new use cases are likely to shape the individual regional trends. Due to the entry of new players, the ability, new technologies, and the expansion of traditional payments infrastructures into the digital world will lead to the growth of the digital payments industry in the upcoming years.
According to Statista,
- In India alone, the total transaction value of digital payments in 2019 amounts to US$64,787 million.
- This total transaction value of digital payments is projected to increase with a CAGR of 20.1% between 2019-2023 resulting in a total value of US$134,588m by 2023.
- Globally, China has the highest value of digital transactions at US$1,570,194m in 2019.
New technologies will lead to new use cases of digital wallets
When it comes to mature markets, a combination of NFC/contactless technology and mobile payments may lead to the development of new payment use cases. Countries such as Australia, Canada, and the U.K. are exhibiting this trend. Further, as new technologies like IoT and Blockchain are adopted by a greater volume of enterprises, the digital wallets industry will disrupt.
In the future, many more use cases of IoT and blockchain are expected. Firms such as mobile payment company Abraare are experimenting with blockchain technology to enable mobile P2P payments and cross-border payments. Blockchain also can be leveraged for digital cash by mobile wallet providers such as Coinprism and Xapo; the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently embraced blockchain as the basis of digital currency within the country. Further to incorporate IoT enabled payments banks will also create more digital touch points.
In the mobility segment, connected cars may turn into new POS for in-car services, including infotainment and real-time navigation.
OpenAPIs is another breakthrough technology disrupting the digital wallets industry. OpenAPIs provide secure and standardized interfaces across all stakeholders, enabling data to be gathered in one place by aggregators.
Regulators will create policies to enable the digital payments ecosystem
As the new technological innovation is transforming the payments landscape, regulators and central authorities across the globe are taking measures to make the digitization of payments easy. Regulators will work towards creating a level playing field for all stakeholders in addition to implementing consistent standards for cyber-security, data privacy, messaging formats, and interface standardization.
Some such key regulatory and industry initiatives are:
- Regulators on the reduction of risk at banks have given traction to initiatives such as BaselIII’s Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR).
- Cyber-security and data protection are witnessing a renewed focus, especially within the EU through the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Network and Information Security (NIS) directives.
- The arrival of PSD2 in early 2018 is expected to meet regulators’ ambitions to create a level playing field for all stakeholders and promote competition by opening the payments market to new entrants in Europe.
The emergence of a collaborative ecosystem
Technological innovations will drive the digital payments industry to evolve and adopt a collaborative ecosystem. As Fintech players and other Third Party Payment (TPP) enterprises give way to better and faster payments interface, banks are opening up their platform to these enterprises. Some of the players like PayU have already acquired Citrus Pay to become a larger group. This consolidation was aimed to expand into more offerings around banking and other services.
Further, new entrants into the payments space, are increasing competition and forcing payments services vendors to consolidate to capitalize on economies of scale. Some examples of such collaborations would be Fiserv acquiring Monitise and PCLender to provide a broader range of customer offerings, and banking players Misys and FIS integrating operations.
In the coming years, the industry will see more such consolidations and Payment vendors with advanced digital capabilities could become acquisition targets as incumbents look to scale up operations to make the most of the expanding digital payments market.
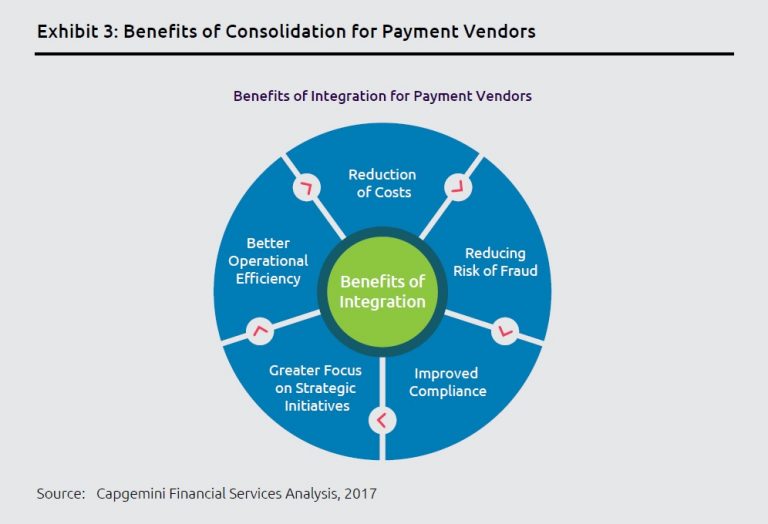
Image source
Stringent data privacy laws will be established:
In recent times, data breach cases and cyber-attacks like WannaCry Ransomware have created the need for more stringent data privacy and security laws.
The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) and New York Department of Financial Services’ regulation on cyber-security are already in place, and more regulations from different central authorities are expected with steep penalties for non-compliance. Further, the U.K. announced a data-protection bill24, which gives more control to consumers on their data. China’s new cyber-security law includes liabilities such as suspension of business activities and fines up to 1 million RMB for violation.
The growth of the cyber-security industry is also a sign of increased emphasis on cyber-security. According to a Forbes report, The overall spending on cyber-security services and products increased over $114 billion in 2018, a rise of 12.4% as compared to 2017. The report further states that the cyber-security investment will continue to grow by 8,7% to $124 billion.
The digital wallets and mobile payments industry will expand in the coming years owing to the infrastructure becoming more robust, enablers like NFC, POS acceptance devices and online integrated mobile payments.
However, security, ease of transactions and enabling multiple transactions on a single platform will be of key importance in gaining more users. The digital payments ecosystem is on a growth curve, and a collaborative ecosystem with financial services, Third Party payment vendors and Fintech enterprises will emerge in the years to come.















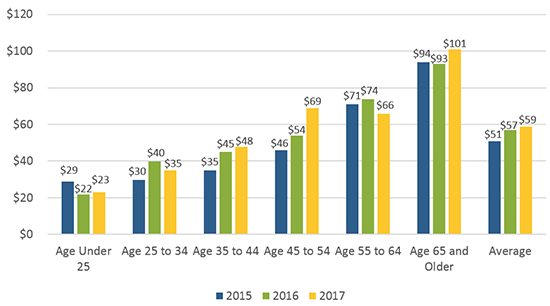











 Image
Image