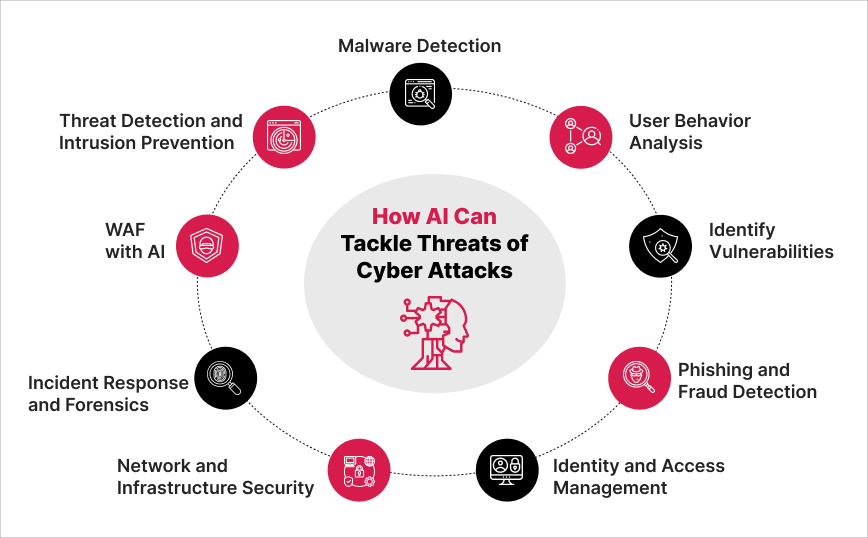
The swift expansion of the digital economy has resulted in a notable increase in digital crimes. Industry reports indicate that companies face annual costs in the trillions to address cyberattack damages. Adopt the ISO27001 framework to design a Cybersecurity framework program for your organization.
By the end of 2023, Cybercrime Magazine predicts a colossal $8 trillion in yearly cybercrime damage costs. This surge in the frequency and sophistication of attacks places cybersecurity at the forefront of modern business concerns. It highlights the acute need for organizations to manage risks by adopting a robust cybersecurity framework.
IT Landscapes are Growing and Becoming More Complex
As business leaders accelerate digital adoption, the IT landscape is expanding, accompanied by increasing security challenges. Additionally, the adoption of hybrid work models adds complexity to IT networks.
The increased use of advanced AI and ML technologies by attackers to plan sophisticated cyber-attacks, the surge in machine and IoT identities, the increase in the interconnectivity of Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology, such as shop floor equipment, etc., and the rise in cloud adoption expands the growing risk landscape.
Hence, adopting a structured approach to creating a cybersecurity framework is essential.
The Imperative for a Systematic Approach
Basic security measures such as firewalls and antivirus software cover some aspects of security and provide some level of defense. However, these measures do not cover other security aspects such as application security, end-point security, etc. Therefore, they are the ad-hoc approach. Hence, we require a systematic approach to cybersecurity.
Creating The Cybersecurity Framework – Compliance-led approach
A cybersecurity strategy that prioritizes a compliance-led approach helps align an organization’s security practices with established industry standards. This ensures that security controls are in place to nullify all potential attack options. Thus, organizations adopting a compliance-led approach to steer their cybersecurity strategy can ensure regulatory compliance, holistic security, reduced risk, robust data protection, and data governance.
To develop a compliance-led approach, organizations must comply with multiple standards beyond just one to cover all security aspects. For instance, ISO 27001, NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology), or Mitre Attack lay a foundation, industry-specific standards like Health Insurance Portability and Accountability (HIPAA) for healthcare and PCI/DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) for credit card industries, demonstrate the need for a tailored approach.
While these standards prescribe a general approach and controls, adapting the standards to align with the organizational security needs is essential to creating a cybersecurity framework.
Key Elements of a Cybersecurity Framework
- Discovery and Cataloging: Identifying assets, processes, systems, and stakeholders.
- Data Classification: Assessing the value of each information asset.
- Data Value Quantification: Evaluating and assigning values to the likelihood and impact of identified risks.
- Vulnerability Identification: Identify Vulnerabilities in the organization’s IT and OT systems.
Discovery and Cataloging
Discovery
Data discovery involves identifying, collecting, and analyzing data. The steps involved are:
- Identify the data sources.
- Understand system usage and its accessibility, determining who accesses it (such as user groups and applications) and their level of access.
- Categorize the data based on the types of value it can create, such as:
- Financial value: Data that can generate revenue or reduce costs.
- Operational value: Data that can improve efficiency and productivity.
- Strategic value: Data used to develop new products and services, identify new markets, and make better decisions about resource allocation.
- Investigate the interdependency of data, its origins, integrations, and usage.
Cataloging
Data cataloging is crucial for enhancing data comprehension, improving data quality, and implementing governance policies such as retention, access control, and more. It involves:
- Creating a data map.
- Analyzing and constructing a data dictionary that includes:
- Data element groups (e.g., Employee, Payment, Receivables, Procurement, Operational).
- Information groups (e.g., Employee Salary-related, Vendor financial information, customer details).
- Data sources (System names where data resides).
- Dependent systems (Systems utilizing this data element).
- Brief descriptions of data elements.
- Compliance mapping (identifying applicable compliance requirements).
- Storage types (e.g., data field, image, PDF).
- Storage locations (e.g., Vendor app cloud, MN8 database, or cloud).
- Data owners (e.g., HR, Finance, Operations).
- Retention duration (length of data history maintained).
Data Classification
Data classification, often under-emphasized in cybersecurity, determines an organization’s data value. It guides the direction of cybersecurity investments for the highest return on investment. Allocating substantial funds to protect critical data (‘crown jewels’) is more effective than securing all data, especially when the loss of some data would have minimal monetary impact on the organization.
It’s crucial to differentiate between high-value and less critical data, organizing and labeling them effectively. For this purpose, leveraging artificial intelligence and other advanced technologies can be highly beneficial.
Data that is high-risk or sensitive needs extra care. Ask yourself the following questions to help lower the risk of data breach or loss:
- Do I need to make a copy of restricted data?
- Do I need to share restricted data with someone else?
- How long must I keep a copy of restricted data?
Data Value Quantification
Organizations must clearly understand and quantify the value of their data. This crucial step guides allocating effort and financial resources toward data protection. The process includes:
- Estimating the nature of potential attacks, such as data theft or data unavailability.
- Assessing the annual likelihood of such incidents.
- Calculating the annual monetary loss – the Risk Amount – by combining the data’s value and the estimated incident frequency.
With the financial quantification of risks, organizations can prioritize and focus spending on protecting their most valuable data.
Vulnerability Identification
Identifying systems, software, and network vulnerabilities is crucial to mitigate risks before attackers can exploit them. Various methods are available for this purpose:
- Manual Techniques: These require prior knowledge of the existing systems, software, networks, and their vulnerabilities.
- Automated Tools: A range of automated tools can scan systems, software, and networks for known vulnerabilities.
- OSINT (Open Source Intelligence): This method identifies potential vulnerabilities by gathering information from publicly available sources, such as websites, forums, and social media. It also includes threat intelligence from cybersecurity firms, government agencies, and private sector organizations.
Creating a Security Framework Leveraging Compliance Standards
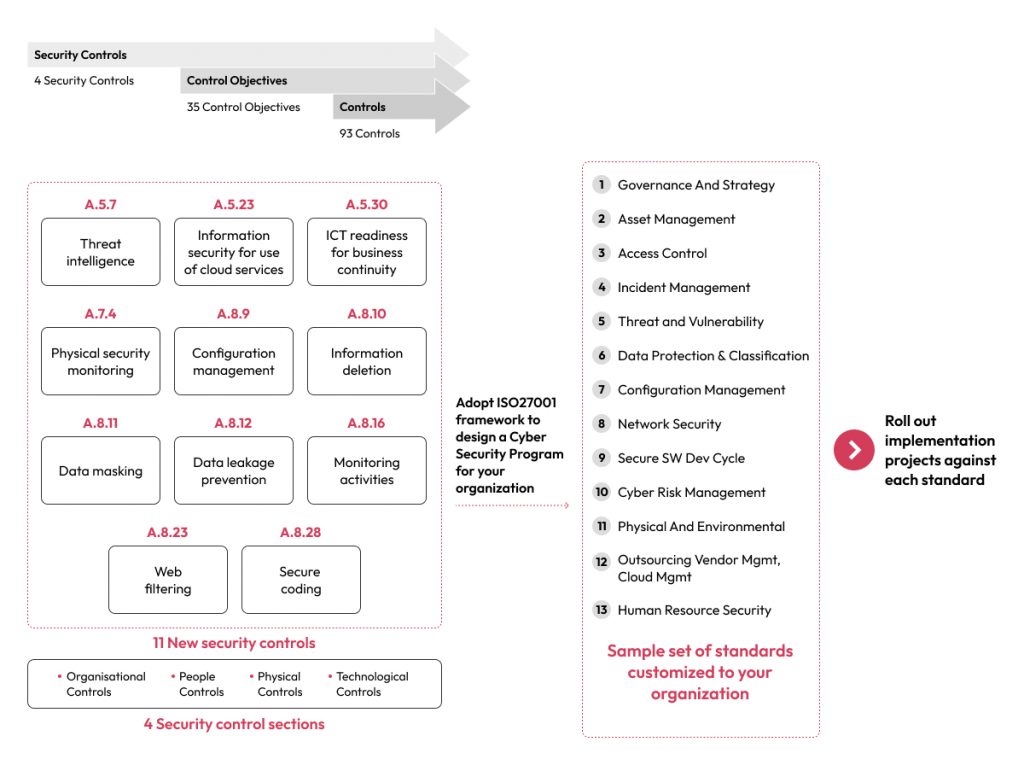
The diagram below represents the 4 security control sections and 11 new controls out of 93 controls prescribed by the recently updated version of ISO 27001 (the previous version of ISO 27001 included 14 security controls comprising 114 controls). Organizations adapt and adopt these controls depending on their maturity level to formulate a Cybersecurity Framework (CSF). The CSF outlines policies and procedures and encompasses five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. In line with the above, organizations actively implement projects that align with these standards, thereby managing controls more effectively.
The Benefits of a Compliance-Led Cybersecurity Approach
A compliance-led cybersecurity approach offers numerous advantages for organizations, particularly those operating in highly regulated sectors. Here are some key benefits:
- Regulatory Compliance: Achieving and maintaining regulatory compliance shields organizations from legal repercussions and ensures adherence to industry-specific standards.
- Data Protection: Robust security measures safeguard critical data, reducing the risk of breaches and unauthorized access.
- Reduced Risk: Strong security protocols protect vital data, minimizing the chances of breaches and unauthorized entry.
- Improved Data Governance: Clear data governance policies enhance data quality and management in addition to security.
- Holistic Security: A comprehensive and structured approach leaves all vulnerabilities addressed.
- Business Continuity: Incident response and recovery plans ensure uninterrupted operations in the face of cyber incidents.
As we move forward in the digital age, it becomes increasingly clear that cybersecurity is not just a defensive measure but a strategic imperative. The insights discussed in the blog demonstrate the necessity of evolving with technological advancements and emerging threats. A comprehensive cybersecurity framework is the cornerstone of safeguarding an organization’s digital assets and fostering a culture of innovation and resilience.
With data as valuable as currency, such a framework becomes a key differentiator in the marketplace. It enables organizations to pursue new opportunities while securely and confidently managing their digital footprint. Adopting this proactive approach to cybersecurity positions organizations as defenders and pioneers in shaping a secure and sustainable digital future.
The Robosoft Advantage
At Robosoft Technologies, we recognize the importance of both compliance-led and risk-based cybersecurity strategies. Our expertise in Cybersecurity, covering areas such as Application Security, Cloud Security, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), and Data Security, positions us as your ideal partner to strengthen your cybersecurity posture. Reach out to us today to fortify your organization against cybersecurity threats.