The approximate cost of drug discovery has reached $2.6 billion, which is a tenfolds increase in the last decade. Clinical trials are an important aspect of the drug discovery process and also adds to this cost. It has become extremely critical for the pharma companies and the CROs (Clinical Research Organizations) to adopt technologies that can optimize these costs and enable a faster and secure critical trial process.
The data generated in Clinical Trials is crucial in the preparation of peer-reviewed journal papers and approval applications for regulatory bodies. Therefore, data validation, data management, and data integrity play the most important role in Clinical Trials.
There are several impediments to the validity of Clinical Trials data. For instance, loss or alteration of data, redundant and non-transparent database management systems, data duplication and manipulation, etc.
There is a need for the industry to adopt technologies that can accelerate the pace of data validation, help in managing higher standards of data transparency, and maintain stricter fraud prevention practices. Blockchain and its Hyperledger Fabric framework, are now emerging as a technology that the industry has started to explore to solve for these issues.
In this article, we will outline how the open-source blockchain framework, Hyperledger Fabric can help in creating a more efficient, secure, and faster Clinical Trial process.
The Challenges of data management during the Clinical Trial process
The end-to-end Clinical trial process, including the preclinical phase, often can be lengthy and expensive taking 10-15 years to complete, with the median cost reaching approximately $19 million. Further, it requires communication between multiple stakeholders including academic researchers, journal editors and publishers, drug and device companies, government regulators, patients, etc. This increases the complexity of the clinical trial process, in terms of data collection, data management, data integrity, etc.
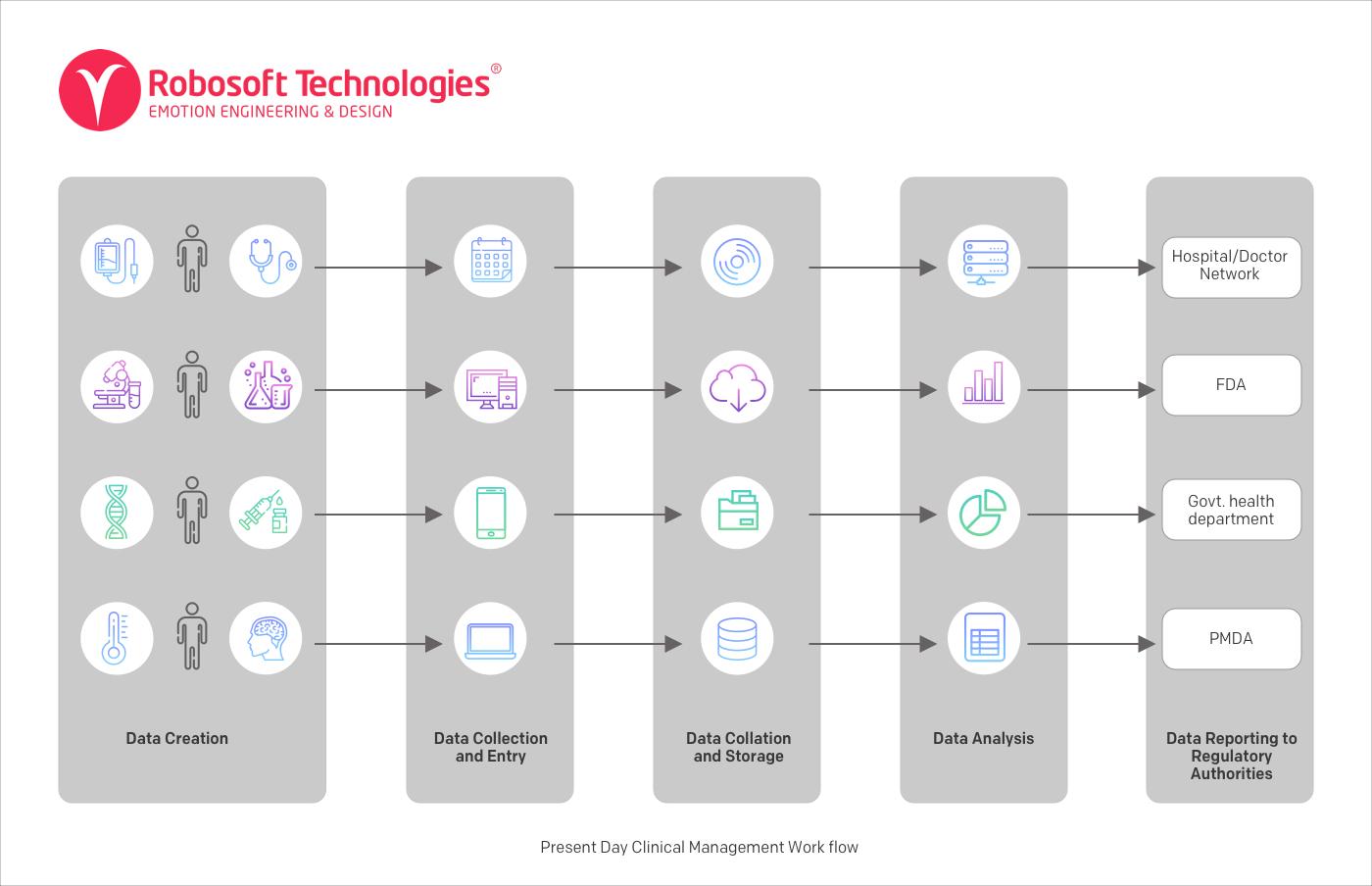
Sample clinical management workflow – Data source
In this kind of Clinical Trials process, the different stages of Clinical Trials are conducted independently of each other. This is often due to the legacy technology and legacy approach to conducting Clinical Trials.
In this system:
- Data is created at multiple channels – hospitals, Clinical Trials, smart devices, etc.
- Data is then collected and stored in an organization-specific Centralized Database Management System (DBMS).
- Different stakeholders like pharmaceutical companies, hospitals, CROs, Biotech, laboratories have their own decentralized databases.
- Different organizations then collate and store data in their own preferred way and own preferred format in their own IT environments.
- Data is then analyzed separately within each organization and results are presented to regulatory authorities.
In this model, collaboration is not only difficult between multiple parties involved in the process, but collaboration is also difficult within organizations.
Given the complexity of the ecosystem, the Clinical Trial process is faced by many challenges from data management to scalability. Some of these are:
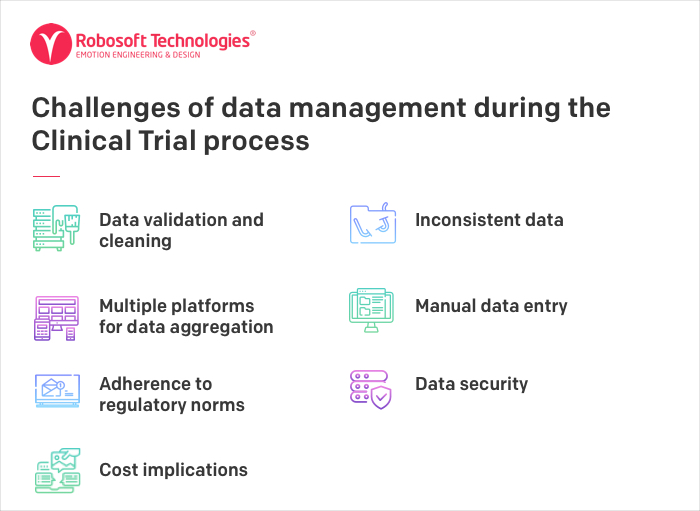
Data validation and cleaning – Clinical trial professionals spend a huge amount of time in cleaning and preparing data to meet the demands of the evolving pharma and the life sciences industry. According to a study by Oracle, data completeness, data quality and data cleaning remain the topmost operational challenges for Clinical Trial professionals.
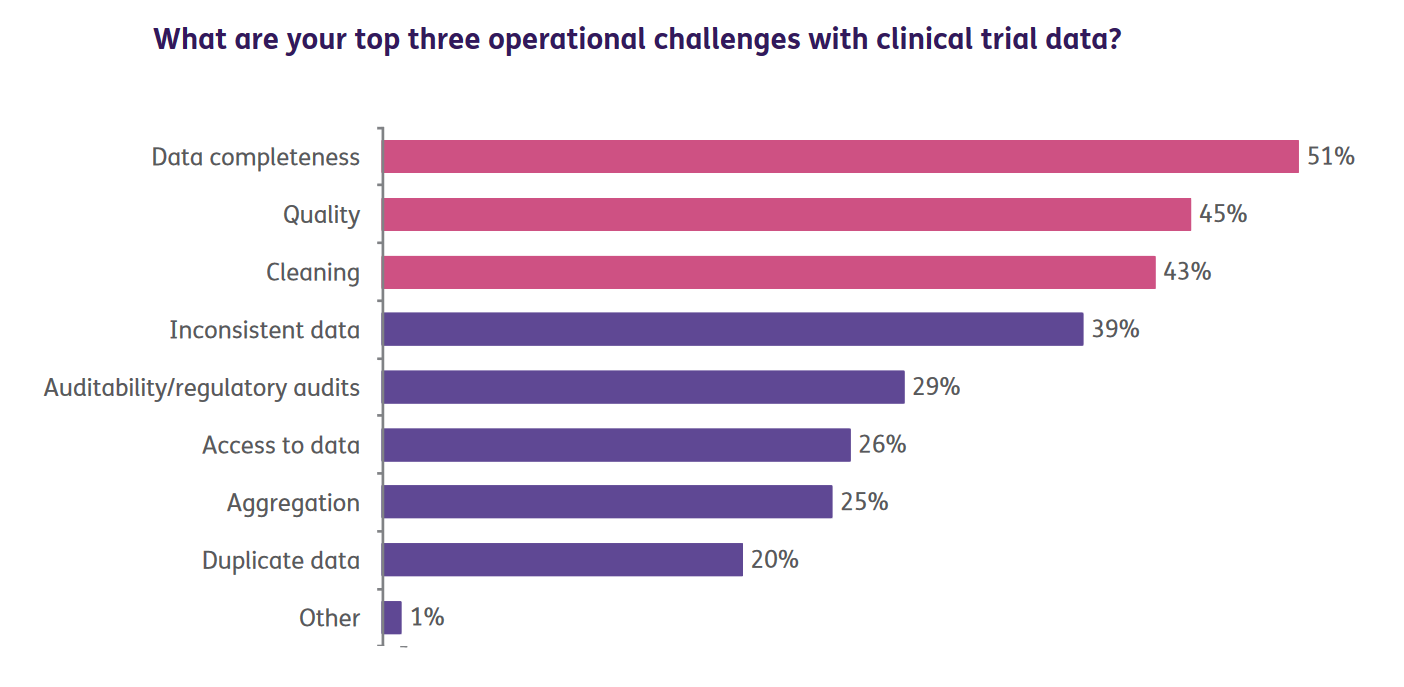
Image source
The quality of the trial data can be affected by a number of factors like missing data, endpoint switching, data dredging, selective publication, etc.
Inconsistent data – During Clinical Trials multiple versions of data are created from sources like external labs, CROs, other vendors. This system gets increasingly complex with the globalization of Clinical Trials. The storage of data in siloed systems which leads to duplication and creates difficulties in accessing the required data.
No single platform of data aggregation – Clinical data is not easy to access, due to multiple sources of data collection. This leads to a huge amount of time spent by researchers in finding answers to research queries, which needs pulling data from a variety of sources and reports.
Manual Data Entry – The systems which have manual data entry do not allow for automatic integration with a broader record and thus investigators are not able to analyze data in real-time.
Adherence to regulatory norms: Clinical trial processes need to adhere to regulatory authority compliant system such as 21 CFR Part 11. Often necessary regulatory processes slowing research because timely approval is not given for data use.
Another issue faced by the US Food and Drug Administration is updating of data by the publicly-funded Clinical Trial labs. According to the FDA, all the publicly-funded Clinical Trial labs should submit the data done on human subjects to the designated public repositories. While portals like clinicaltrials.gov allow the depositing of research data with the help of services like Fighare, only a few research groups follow this. And even if they do follow they seldom to it consistently over a long-term, leading to missing information.
According to a report on Forbes, it is estimated that 50% of Clinical Trials go unreported, and investigators often fail to share their study results (e.g. nearly 90% of trials on ClinicalTrials.gov lack results). This may result in crucial safety issues for patients and create an information gap for healthcare stakeholders and health policymakers.
Data security: The Clinical Trial data is sensitive and preventing data leakage, fraud and misuse of confidential data are of prime importance. Hence, data verification through multi-party channels is required. Further, ensuring that data sharing is consistent with federal and local regulations is also one of the challenges that the industry faces.
Cost implications: Due to the complexity of the Clinical Trials process and the above issues, the cost of conducting Clinical Trials is high. Further, the tight delivery timelines put additional pressure on the Clinical research professionals and CROs
How Blockchain Technology can help to solve these issues
The BFSI sector has been long facing the issue of data attrition and data fraud, and Blockchain Technology has been one of the solutions that the sector has been looking forward to. In a digital era, technologies are no longer limited to one industry and the healthcare sector too is starting to explore the benefits of blockchain in various areas and Clinical Trials are one of them.
Blockchain technology is a peer-to-peer distributed ledger-based system where the information is stored in a distributed shared ledger, which can only be manipulated by something called transactions. Transactions are digitally signed and encrypted form of communication between the client and the blockchain app.
There are various Blockchain frameworks available like Entehreum, Hyperledger Fabric, R3 Corda, Ripple, Quorum, Multichain, BigChainDB, and Chain. Ethereum and Hyperledger Fabric are the two most popular frameworks.
In our recent webinar – Introduction to Hyperledger Sawtooth: An open-source enterprise blockchain platform, we simplified the concept of blockchain and helped participants understand how Hyperledger Sawtooth can be implemented for businesses – with a live demo. You can watch the replay of this webinar here.
Ethereum vs Hyperledger Fabric and why Hyperledger Fabric is better suited for Clinical Trials
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is an open-source blockchain platform where decentralized applications can be built using Smart Contracts. As the Smart Contracts on which Ethereum runs are decentralized, they are open to everyone in the network. This aspect is not favorable for privacy-conscious data that the Clinical trial ecosystem deals with.
The Clinical Trial ecosystem is complex with multiple stakeholders requiring time-sensitive inputs. And, a secured framework consisting of multiple private blockchains with different properties and shared data accessed by various stakeholders, can help streamline the Clinical Trial process.
This is where a Hyperledger framework comes into the picture.
What is Hyperledger Fabric?
Hyperledger is a collaborative project supported by the Linux foundation. It is modular and pluggable and consists of open-source blockchain and related tools with a number of frameworks and distributed ledgers.
Hyperledger Fabric is a permissioned blockchain framework. A permissioned blockchain (also called a consortium or federated blockchain) is a hybrid of public and private blockchain frameworks. On a permissioned blockchain, transactions or data is visible only to the parties with permission to view them — not the whole network.
Why Hyperledger Fabric is better than Ethereum
The key difference between Ethereum and Hyperledger Fabric is that the former is a public or permissionless blockchain where anyone with an open source software can be a participant. While advantages are anonymity and transparency, but the tradeoff is privacy and scalability. This is why Ethereum is more suited for B2C environments.
Hyperledger Fabric’s private or permissioned blockchain protocol allows for authentication, authorization, and permission of actions. That makes Hyperledger Fabric more suitable for businesses in industries like healthcare, which demands collaboration with multiple stakeholders in a secure ecosystem. Further, the modular architecture allows Hyperledger to be more flexible and enables customization.
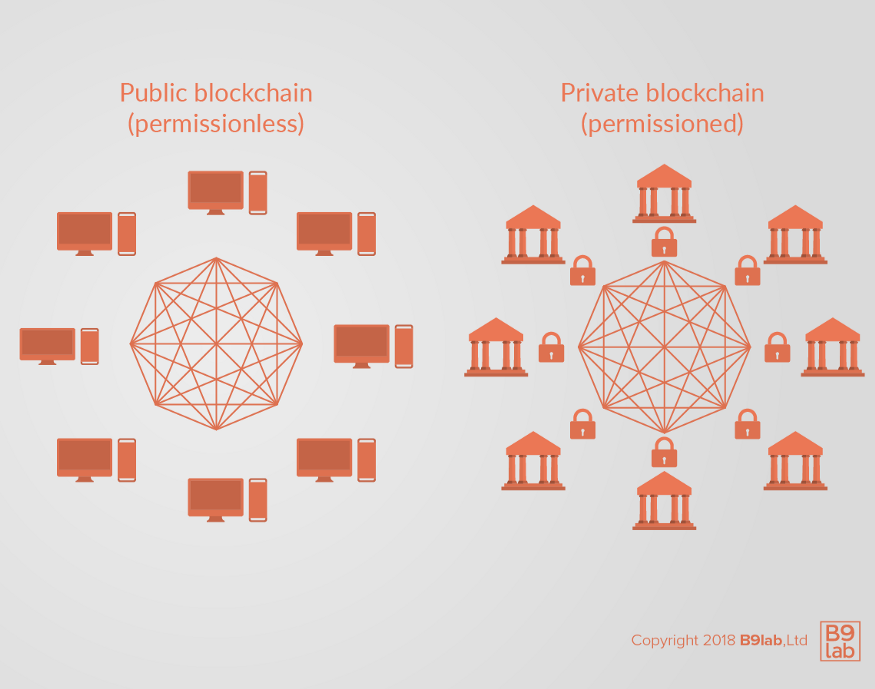
Image source
Blockchain taking a leap in digital health with Hyperledger Fabric
Hyperledger Fabric, released in 2017, is the first publicly available version of the Hyperledger consortium’s open-source blockchain framework. It is a framework based on a plug-and-play environment for building blockchain applications. Some of its features are modularity, container technology to host smart contracts called chain code, which comprises the application logic of the framework.
Last year, Change Healthcare launched Change Healthcare Intelligent Healthcare Network using Hyperledger Fabric 1.0. It is the first blockchain solution for enterprise-scale use in healthcare, enabling payers and providers to boost revenue cycle efficiency, improve real-time analytics, cut costs, and create innovative new services.
Medicalchain a decentralized platform aims to create a platform for different healthcare agents to request permission to access and interact with medical records. Each interaction on the platform is auditable, transparent, and secure, and will be recorded as a transaction on a distributed ledger. The project will guarantee privacy since it will be built on the permission-based Hyperledger Fabric architecture providing for varying access levels
It has some key properties that make it an ideal distributed ledger which makes it easier for the CRO’s and pharma companies to adopt blockchain.
The key features of the Hyperledger fabric are
Assets: Asset definitions enable the exchange of data.
Chaincode: It is a ‘smart contract’ which allows users to create transactions in the shared ledger network of Hyperledger Fabric.
The immutable shared ledger: this can encode the data history of each channel, a include a SQL-like query capability for efficient auditing and dispute resolution.
High level of privacy through Channels: Channels allows multilateral transactions with high levels of privacy and confidentiality required to maintain the strict standards of regulations for the pharma and life sciences industries when assets are exchanged on a common network.
Security & Membership Services: The Fabric platform allows for a permissioned membership provides a trusted blockchain network.
Consensus: A flexible and scalable approach to consensus.
Advantages of using Hyperledger Fabric for Clinical Trials

Data security and privacy
Using permissioned blockchains like Hyperledger Fabric ensures that only authorized organizations/entities with designated permissions as defined by a set protocol can join the network(s) and perform only certain activities on the network. In Hyperledger Fabric HSM (Hardware Security Module) provides a way to keep private keys secured. These private keys are not outside of the HSM thus ensuring greater security. This approach can provide sources guaranteed anonymity required for PHI (Protected Health Information) and a fully audited verification of the data.
Regulatory compliance
Permissioned blockchains can achieve data privacy and security compliance such as HIPAA or PIPEDA as data is stored only on authorized “nodes”. Hyperledger Fabric is a framework where all participants have known identities. The healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and life sciences industry, is subject to data protection laws that require knowing the identity of the members of the network and who is accessing specific data. Creates a Private Permission structure for the patients, allowing them to use SSO (Single sign-on) to hide and maintain their anonymous status in all data exchanges.
Optimized costs and faster process
With a private and permissioned blockchain framework like Hyperledger Fabric, computationally inexpensive protocols can be used for verifying transactions. Leading to faster and significantly cheaper processes. It enables the analysis of data from multiple trials, as well as leveraging data stored by different sources, in different locations. Creating a cost-effective virtual data universe (Data Lake).
Increased performance, scalability, and levels of trust
Due to the modular architecture of Hyperledger Fabric data processing is distributed into three phases: distributed logic processing and agreement (“chaincode”), transaction ordering, and transaction validation and commitment. This distribution needs fewer levels of trust and verification across node types, and thus network scalability and performance are optimized.
As IBM describes it, Fabric “is designed to provide a framework for building enterprise-grade blockchain networks that can quickly scale as new network members join and transact at rates of more than 1,000 transactions per second among large ecosystems of users.”
In conclusion:
Clinical trials are one of the most crucial parts of the drug discovery process. As the time and the cost of the clinical trials rise, it hinders the drug discovery process.
The distributed ledger and permissioned framework of the Hyperledger Fabric based blockchain app can help in creating a more efficient Clinical Trial process by maintaining Clinical Trial integrity, manage data efficiently, manage data transparency and security, and achieve data compliance. It can lead to the structuration of community-driven health data, decentralization of the process, and manage higher security and with transparent interactions to ensure an easier and more transparent process.




