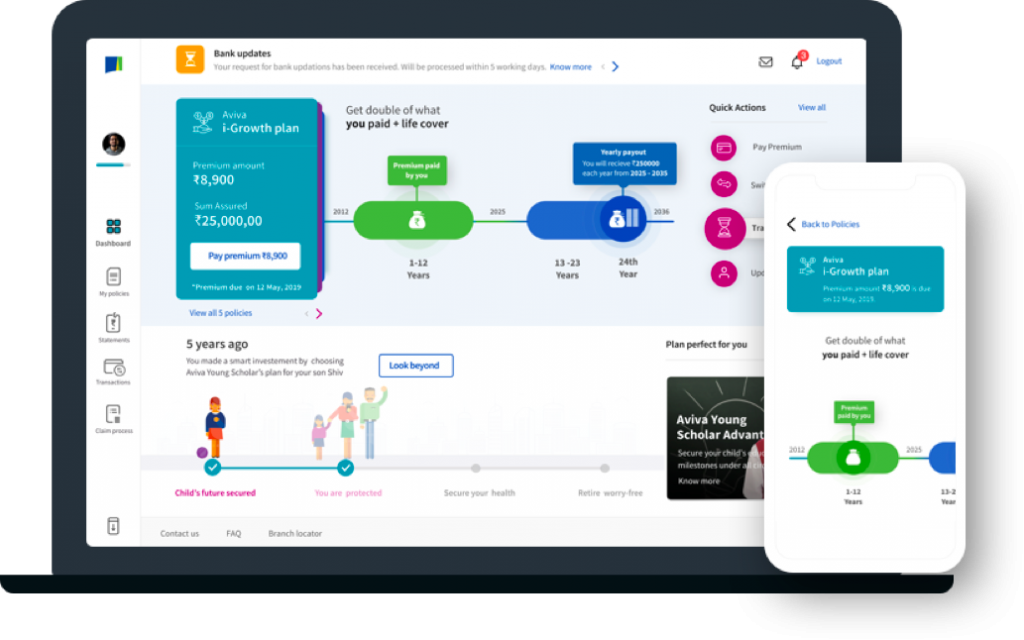
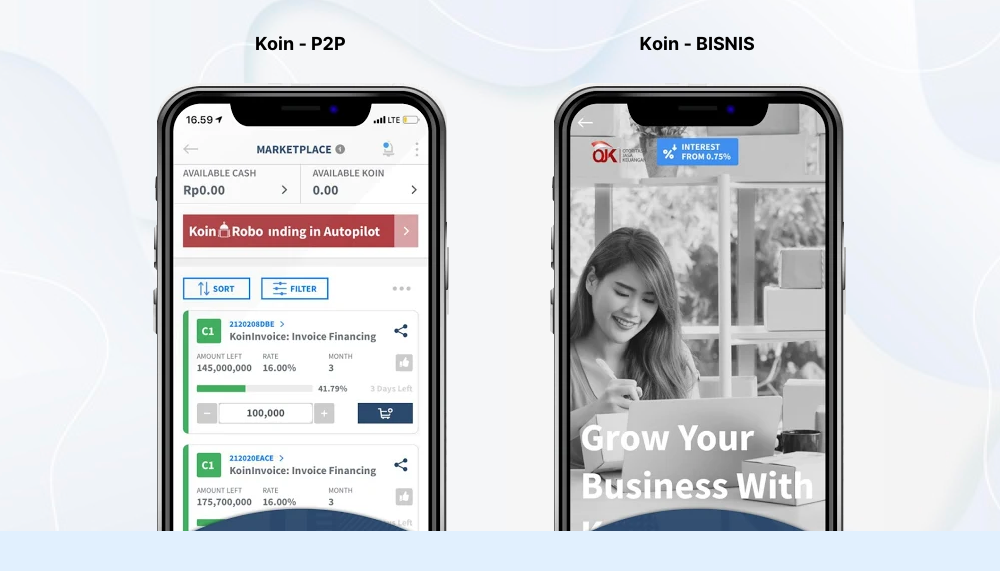
As an industry, insurance is often considered to be evergreen in terms of profitability. However, while demand for insurance has grown globally, insurance providers are facing a number of challenges that affect profitability.
According to a McKinsey report, profits reduced by around 15 percent compared to 2019, and premium growth had slowed to around 1.2 percent in 2020, compared with over 4 percent growth in the decade between 2010 and 2020. However, post COVID-19, insurance companies are poised to take advantage of the rebound. Based on a survey of over 424 insurance respondents, the Deloitte Centre for Financial Services reports that insurance companies have an optimistic outlook, while the Swiss Re Institute predicts rising demand worldwide, with premiums for all lines rebounding by 3.9 percent in 2022, as compared to the earlier drop of 1.3 percent in 2020.
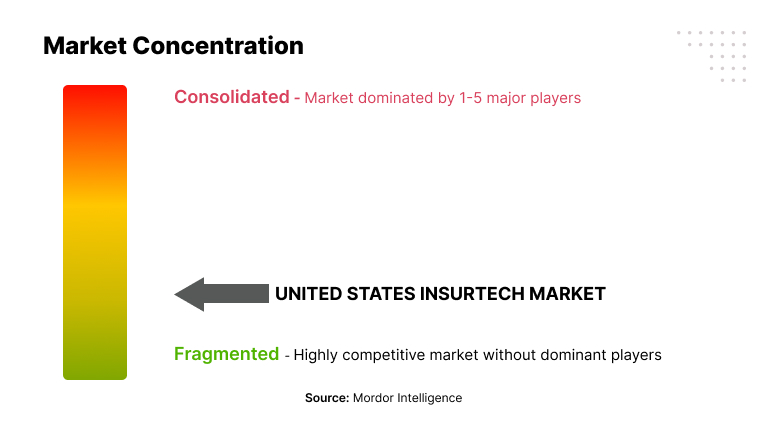
Despite the opportunity, risk factors have increased and insurers are aware of the need to deal with challenges facing the industry and build business resilience. Across the insurance sector, there is a higher claims incidence, leading to increased pay outs and loss of profitability. Insurers need to maintain higher capital because of regulatory pressures. They are also facing increasing competition from new entrants in insurtech.
Property & casualty insurance at a pivotal stage
The US property and casualty (P&C) insurance market is a case in point. Not so long ago it was the pandemic that was keeping insurers awake at night. Now, inflation is putting them to the test. The US holds the biggest market share of P&C insurance and is among the most mature geographies for insurance. However, inflationary pressures are significantly holding down P&C insurance carriers. Although the market grew by a moderate 4.7% between 2018-19, these challenges are dampening future prospects.
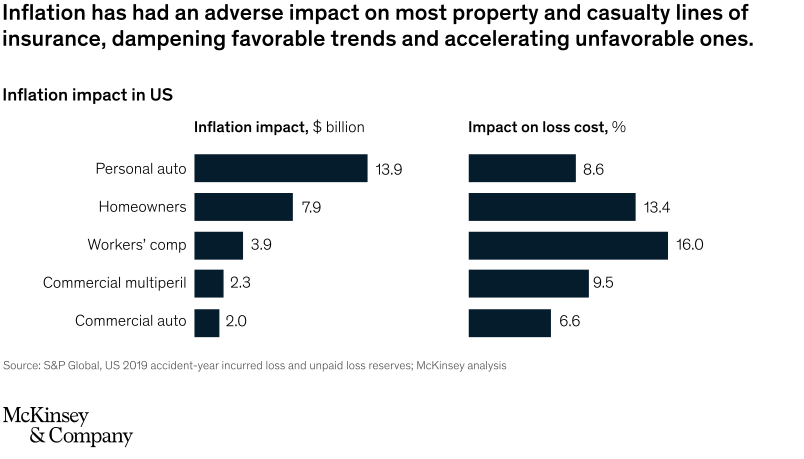
Source: McKinsey & Company
Opportunities in P&C are rising, but insurers are weighed down by market volatility, changing customer expectations, and loss of profitability to name a few. Given the uncertainty of tomorrow, P&C insurers need to build business resilience – the ability to endure present challenges and be ready for future shocks and negative events.
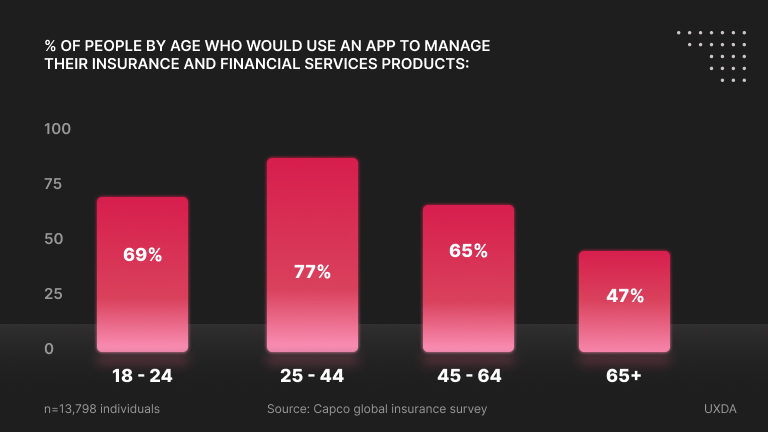
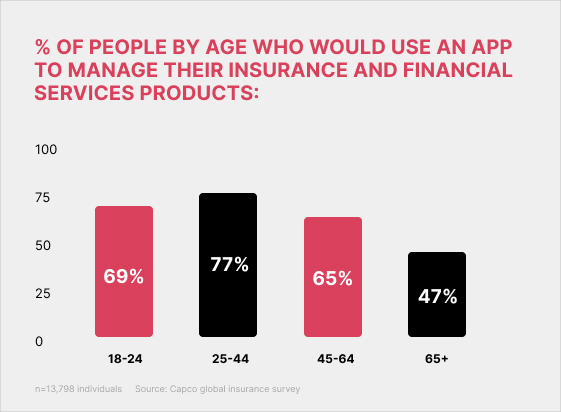
The insurance industry is learning from the success of insurtechs and waking up to the advantages of strengthening customer connections by going digital. One of the biggest positives in recent years is the accelerated digitalization that enables non-face-to-face interactions between the insurer and the insured. Today, customers want more intuitive, user-friendly apps that will help them gain quick access to relevant data that will help make the right choices for their insurance needs, streamline processes, and more. They also expect 24/7 assistance in making decisions. Research indicates that a good number of respondents are ready to move away from insurance companies that do not offer these advantages.
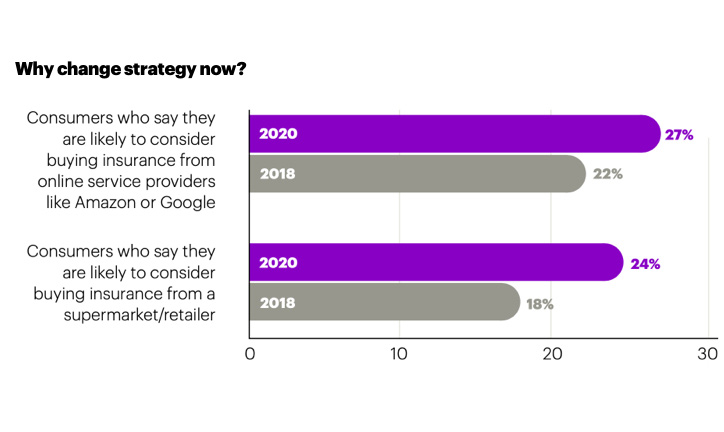
Source: Accenture
Building resilience in P&C insurance with technology
As P&C insurance is complexity-ridden and highly regulated, the way forward needs to be holistic and future-ready. Resilience is key to countering market volatility, inflationary pressures, and intense competition – that means becoming nimble, responsive, and well-prepared for all the odds. These challenges, considered together, call for a major shift in strategy by traditional insurance players.
Technology can provide P&C insurance companies with not just the chance to become more future-ready but also to differentiate themselves using technology. Insurers can adopt digital to create a wider platform that can connect customers, partners, and employees all at the same time. Tech innovation finds application across the value chain from marketing through distribution, products and services, and throughout backend processes from underwriting to claims. Technology can also help design and create memorable user experiences, engaging with customers more deeply with empathetic, hyper-personalized interactions at various touchpoints of the customer journey.
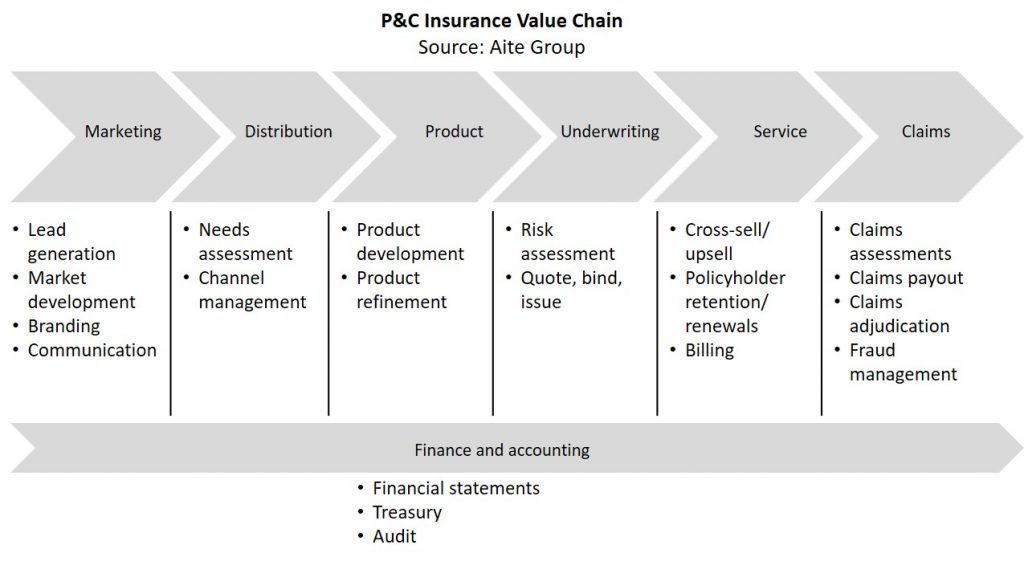
Source: Aite Group
Streamlining claims with automation, AI, and straight-through processing
Automating claims processing, typically a long and tedious task, reduces processing time and cost by programming tools to handle repetitive tasks.
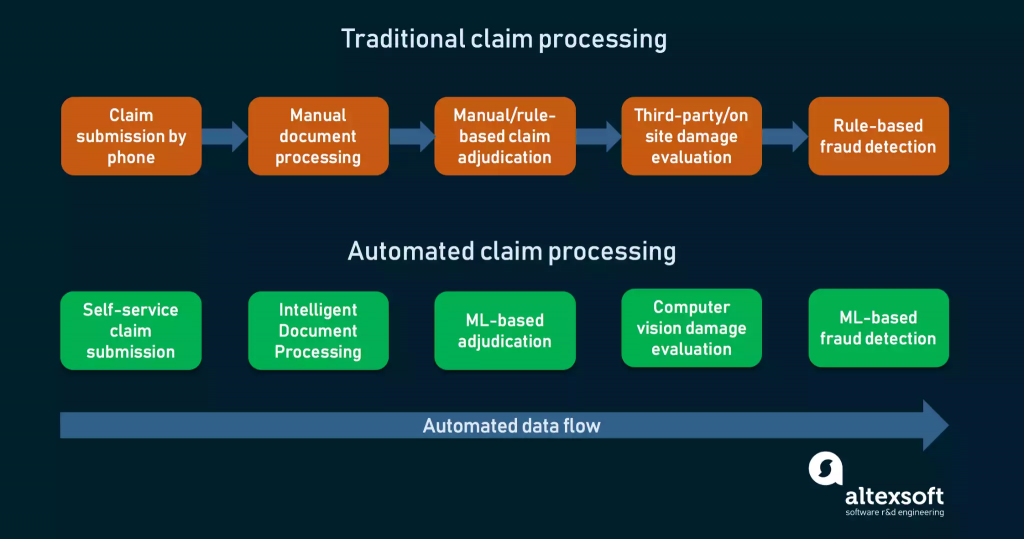
Source: Altexsoft
Self-service in insurance is also becoming popular. One such example is that of easy claims filing online by customers themselves. Apps offer features allowing customers to take photos and upload them while lodging claims for auto insurance from the site of the event itself, enabling remote inspection. This advantage is offered by Bdeo’s AI-enabled platform on their mobile app. In addition, their chatbot uses Natural Language Processing to get reliable information on the accident by ensuring claimants share photographic evidence of acceptable quality on the platform. The insurer uses these inputs as part of their inspection and investigation of the incident remotely. This helps make more accurate evaluations and improves the claim processing experience for both the insurer and claimant.
AI will make it even easier to identify fraudulent claims, as well as provide predictions and estimates of possible damages and extent of losses. In fact, studies indicate that AI has great potential in disrupting core processes including underwriting, claims, marketing by enabling more human-like interactions with customers. Here we illustrate the use of AI in streamlining content extraction that can speed up the processing of claims dramatically while making communication and other value-added services easier to achieve.
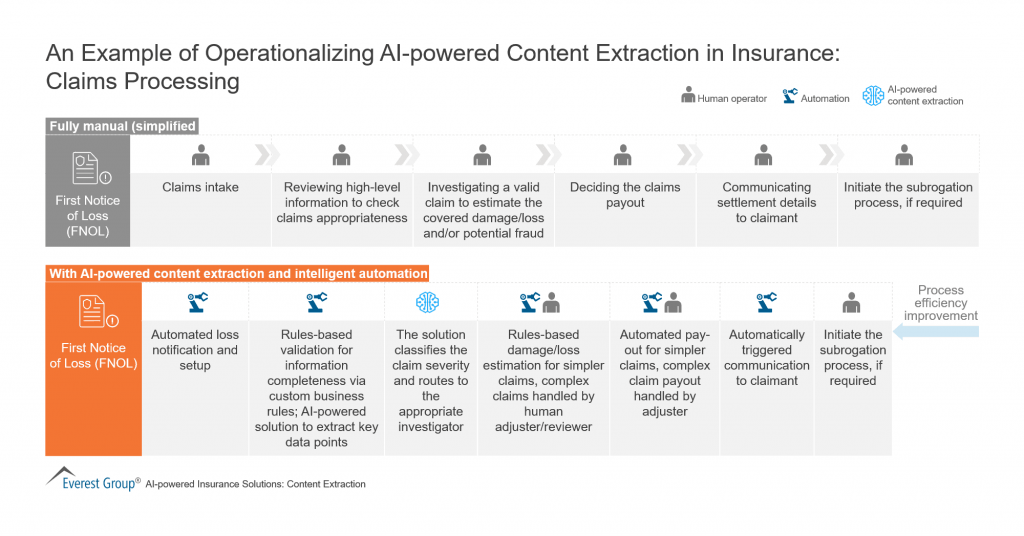
Source: Whatfix
Straight-through processing is another solid investment pathway for insurers – it can be done without any manual input, reduces operational costs, and helps insurers take pricing volatility in their stride. At the same time, policy holders can choose how they want to receive claims settlements in a convenient manner.
Strategic decision-making bolstered by Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Property and insurance carriers tend to be skeptical about RPA, however RPA has proven to drastically reduce errors, improve operational efficiencies, enhance scalability, and optimize headcounts at financially viable numbers. The benefits of RPA multiple when the insurer decides to automate non-strategic tasks while retaining humans to perform value-added tasks. For example, in auto insurance, gathering and validating information around accident claims from various sources such as police reports of accidents, driver’s licenses, photos of damage to the vehicle(s) involved etc. can be tedious and time-consuming, but RPA can comb through data from various sources quickly.
The true potential of RPA is visible when it is collaboratively applied with other technologies to augment strategic decisions made by the human workforce. In the underwriting process, which is again typically lengthy, bots can leverage AI and analytical capabilities to glean information from both external and internal sources, fill up application forms with appropriate data, assess loss runs, evaluate the claimant’s past track record of claims and settlements, and offer pricing based on this deep well of insights – all in quick time. With RPA, it also becomes easier for insurers to keep up with multiple regulatory standards, which are still evolving and ensure compliance.
Driving responsible customer behavior using telematics
Arriving at the optimal price is foremost for 52% of auto insurance customers and 50% of home insurance customers, as per an Accenture study. Giving their customers optimal pricing will instantly create a competitive advantage for insurers. Telematics applications are already being used to great effect for pricing in the automotive insurance space. Now there is scope to use these applications such as vehicle tracking to instruct and control driver behavior and conditions such as drowsiness, for example.
Smart household or property devices that come alive with the Internet of Things (IoT), will come in handy for closely monitoring data such as humidity and temperature, which could potentially cause damage or depreciation to the home infrastructure or property over time. Data and analytics extracted from these devices can be used to plan risk assessment and inspection of large commercial properties with associated risks. Visuals captured via satellite can be used to draw attention to potential risks or causes of damage to property in a cost-effective manner without requiring an in-person visit from the insurer. These insights can be used by insurers to both monitor and suggest pre-emptive measures around potential risky behavior or lifestyle of policy holders.
Smartening up insurer-insured relationships through smart contracts
As early as 2018, BCG research had predicted that smart contracts could help P&C insurers with savings of more than $200 billion per year in their operational costs.
Here’s why smart contracts are the smart option. These are formulated in lieu of physical insurance policies and all associated claims management information using blockchain technology, which stores transactions as lines of code. Tracking, management, and cloud storage of policies, records of physical assets, and claims-triggering events can all be automated and also takes care of user authentication and detection of fraudulent activities. Smart contracts are easily accessible by insurers, reinsurers, brokers, and other parties thus reducing duplication of effort as well as manual intervention and programmed for claims processing actions automatically.
Unlike physical contracts, smart contracts can track insurance claims and hold both parties accountable. These contracts are, thus, inherently more secure and transparent for users, settle payments on approved claims quickly, and go a long way in lifting the trust factor as well as efficiency of back-end operations.
Ensuring omni-channel customer experience with bots and tools
Keeping up a persistent line of communication with policyholders and prospective customers is important for the insurer in terms of business and keeping customers interested. Chatbots can be introduced early in the discovery or pre-sales stages to initiate conversations about product offerings that might be suitable to customers and prospects. Likewise, the customer’s need for 24/7 assistance and quick responses can be met by chat-bots rather than wait for a human team member who can be freed up to address core service areas. They are already proving popular in the auto and home lines of P&C insurance. For example, Lemonade, who is a leading online P&C insurer, extensively uses app-based chat-bots supported by AI. Their bots are able to devise insurance policies and quotes that are tailored to each customer and available directly on the app. They also interact with and field customer queries while helping process claim applications promptly.
Familiarizing customers and employees with digital adoption platforms
Not all employees are tech savvy. Neither are customers. It makes sense for insurers to invest in training to improve agent performance and customer experience. Integrating training tools with the tech stack adopted by the insurer, will help their workforce and customers effectively use the various tools and processes that are now available to simplify the myriad processes that go into insurance. These include walk-throughs, self-help widgets, quick guides, and AI-enabled assistants for employees.
In conclusion
P&C insurance companies have to work through a maze of challenging situations and gaps as they go about strengthening relationships with customers. AI/ML, IoT, telematics, blockchain, and other emerging technologies can offer a wider, more personalized spectrum of benefits by harnessing data, shaping new offerings like social insurance, and more.
In short, technology can be the bridge that makes interactions meaningful and productive for both insurers and those seeking insurance. It remains to be seen how far P&C insurance players are ready to leap in building the bridge that holds the key to the future.