In an era of increasingly intricate financial markets, the advent of Generative AI (GenAI) in asset management represents a paradigm shift. Imagine a scenario where your investment strategies are dynamically honed by an AI that interprets the cacophony of market data into clear, strategic insights. This is not a vision of the distant future but a present-day reality, where AI is the anchor in decision-making, offering a competitive edge in asset management.
How GenAI is transforming asset management
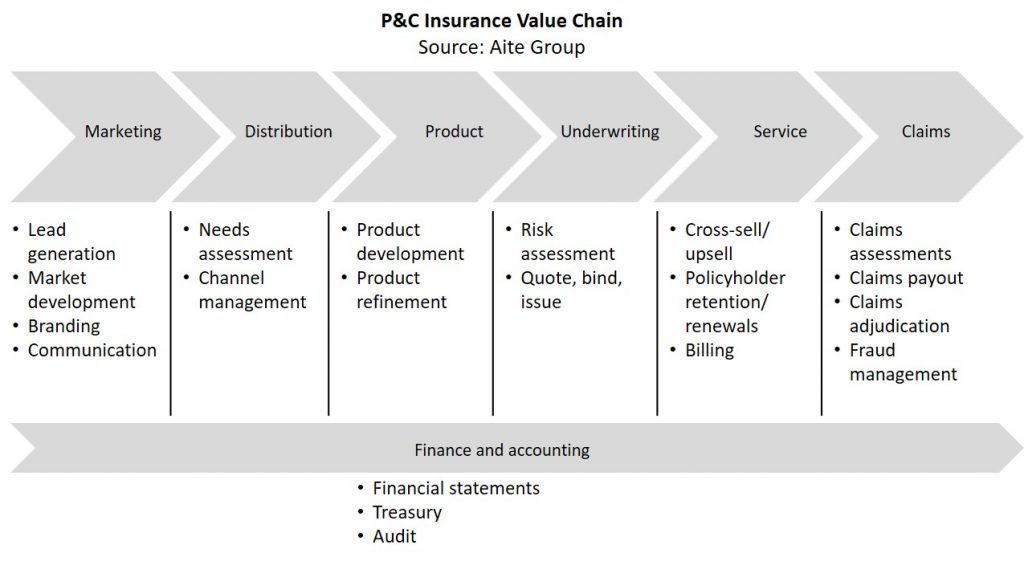
Artificial intelligence (AI) revolutionizes asset management by improving investment decisions, portfolio management, and market trend forecasting. Key AI technologies driving this change include machine learning (ML), which analyzes data patterns for predictions (e.g., stock price movement prediction); natural language processing (NLP), which performs sentiment analysis of news and social media to gauge market sentiment; and predictive analytics, which uses statistical methods and ML to forecast market trends.
Building on these foundational AI techniques, GenAI processes unstructured data, including financial news and social media sentiment, to refine trading strategies and provide deeper market insights.
Here’s how GenAI specifically enhances asset management:
• Portfolio Optimization & Asset Allocation: Utilizes unstructured data to drive insights, deliver market intelligence, and support algorithmic trading.
• Proactive Risk Management: Continuously monitors market conditions, news, and sentiment for early warning signals, allowing for a more dynamic response to market changes.
• Streamlined Client Onboarding: This enhancement enhances onboarding with dynamic e-KYC and bot-assisted self-service options, making the process more efficient and user-friendly.
• Personalized Client Insights: Integrates GenAI with market attribution models and open-source data to provide tailored insights, ensuring investment strategies align closely with each client’s unique needs and risk profiles.
Why asset managers are turning to GenAI
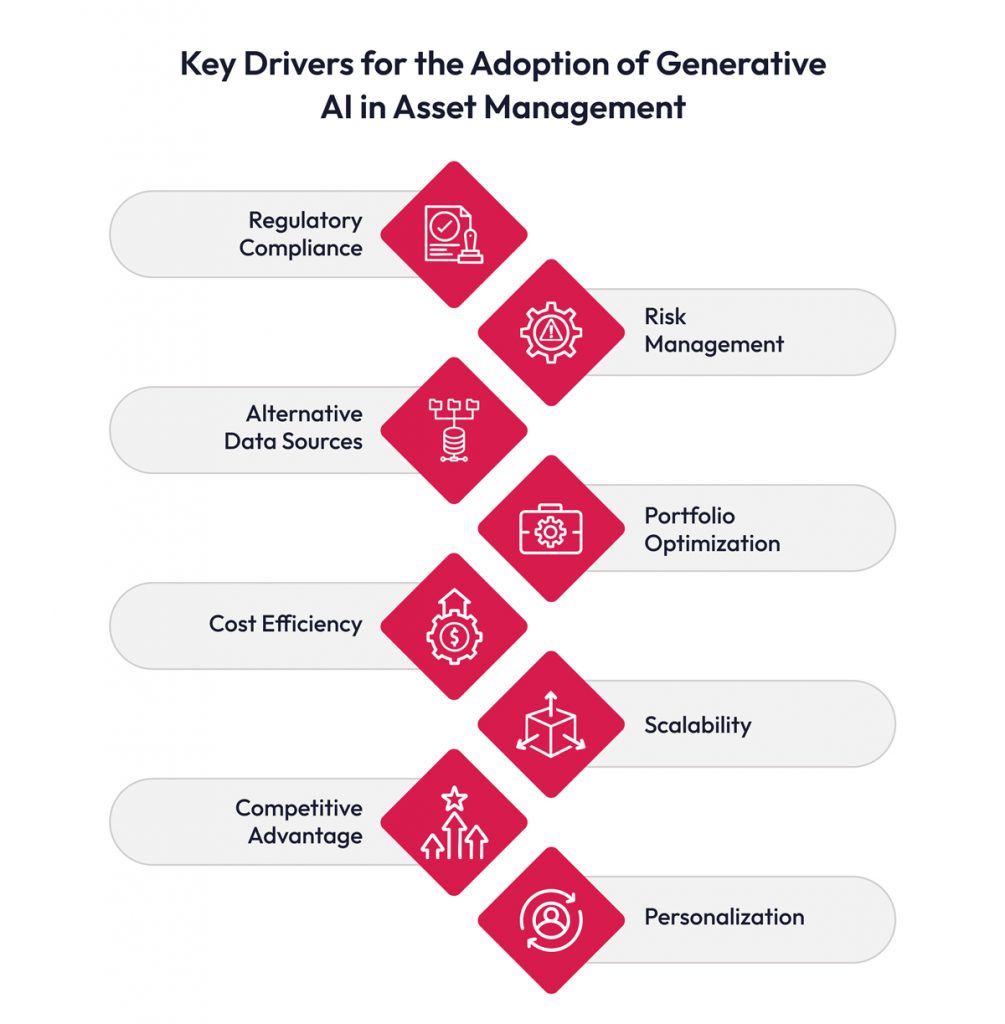
Several key factors are propelling the adoption of GenAI in asset management:
- Data Abundance & Market Complexity: The financial sector generates vast amounts of data daily, and GenAI navigates this complexity by simulating scenarios and identifying investment opportunities.
- Real-time Decision-Making: Enables rapid response to market developments through real-time data processing and analysis.
- Alternative Data Sources: Analyzes diverse data sets, such as social media, satellite imagery, and geolocation, for unique investment insights.
- Risk Management: Enhances risk identification, assessment, and mitigation through scenario modeling and early warning systems.
- Alpha Generation: Identifies non-obvious alpha opportunities by uncovering hidden data patterns.
- Portfolio Optimization: Optimizes portfolios considering risk tolerance, investment objectives, and market conditions.
- Cost Efficiency: Automates routine tasks, reducing operational costs.
- Personalization: Provides personalized investment recommendations based on investor profiles.
- Competitive Advantage: Early adopters gain an edge through superior strategies and higher returns.
- Regulatory Compliance: Assists with compliance by providing auditable records.
- Scalability: Scales to accommodate growing data volumes and portfolios.
Asset management now integrates financial expertise, strategic planning, market understanding, and technology, especially GenAI, for informed, objective-aligned decisions. This integration is driven by market complexities and the need for data-driven decision-making, positioning asset management as a dynamic field.
Advantages of GenAI for asset management excellence
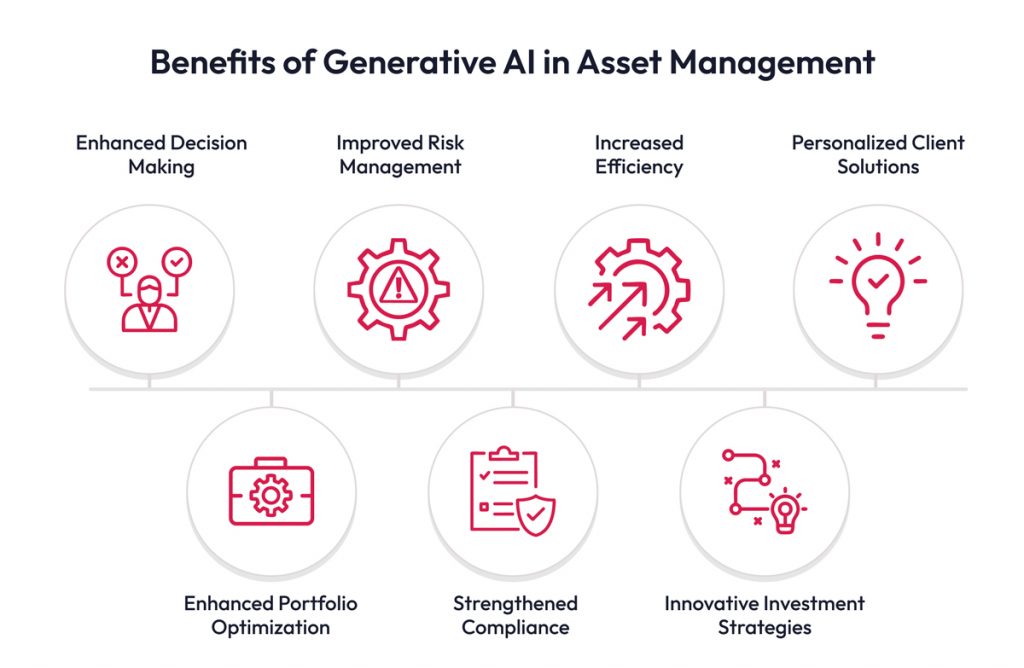
GenAI offers transformative potential for asset management, extending beyond process optimization to revolutionize investment strategies and enhance firm performance. Key advantages and capabilities include:
- Alpha Generation: Leverages advanced analytics to identify unique, risk-adjusted investment opportunities and generate excess returns.
- Personalized Financial Advice: Delivers tailored insights and recommendations aligned with individual client goals and risk profiles.
- Seamless Client Onboarding: Streamlines the onboarding process for a frictionless client experience.
- Optimized Marketing and Investment Operations: Enhances marketing strategies and investment operations through data-driven insights and automation to improve efficiency and ROI.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Generates alternative scenarios, allowing asset managers to explore possibilities and outcomes for more informed investment choices. This data-driven approach reduces reliance on intuition.
- Improved Risk Management: Creates diverse market scenarios, enabling asset managers to assess portfolio vulnerabilities and develop robust risk mitigation strategies.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlines operations by automating data processing, analysis, and reporting, freeing asset managers for higher-level tasks. (Efficiency gains are estimated at 50-80%.)
- Enhanced Portfolio Optimization: Analyzes vast datasets to identify optimal asset allocations, maximizing risk-adjusted returns through AI-powered algorithms.
- Addressing Cognitive Biases: GenAI’s objective data analysis counterbalances emotional biases, promoting more rational investment choices.
- Innovative Investment Strategies: Facilitates innovative strategies by uncovering hidden patterns and correlations through data analysis and scenario simulation.
- Adaptation to Market Dynamics: Enables rapid adaptation to changing market conditions through real-time insights and strategy adjustments.
- Strengthened Compliance and Reporting: Automates data validation and ensures regulatory adherence, enhancing transparency and reducing compliance risks.
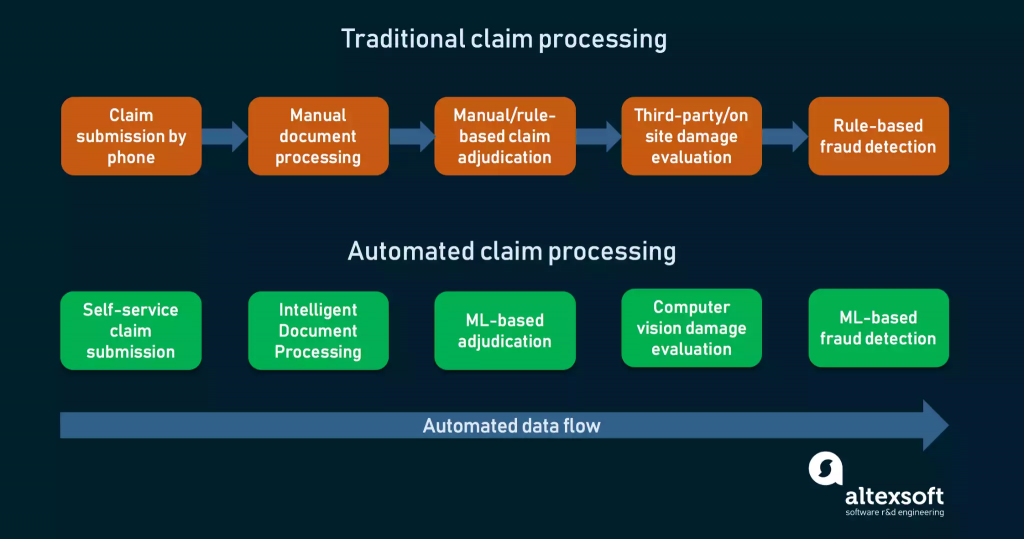
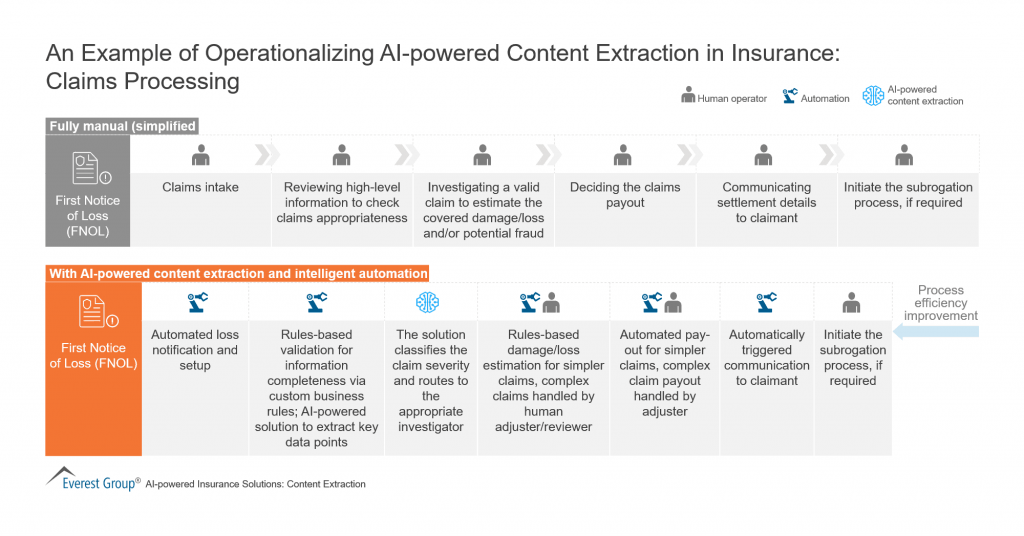
Practical applications of GenAI in asset management
- Data and Predictive Analytics: GenAI advances this by predicting and generating new scenarios or data points. It can analyze unstructured data like news articles and social media sentiment or simulate market responses to hypothetical events. It offers real-time, nuanced insights into market dynamics, shock events, and asset valuation changes, allowing for more proactive and strategic decision-making.
- Portfolio Enhancement and Generation: GenAI goes beyond static analysis by dynamically adjusting portfolio allocations in response to real-time data, including unconventional data sources. It can simulate various market conditions to suggest innovative portfolio adjustments or new investment product designs tailored to specific market conditions or investor profiles.
- Investor Communication and Reporting: GenAI can revolutionize investor communication by generating personalized content. It can create detailed, context-aware reports or interactive dashboards that adapt to the individual investor’s interests, questions, or preferences, enhancing engagement and understanding.
- Operational Automation: GenAI significantly transforms operations by automating routine tasks and creating new processes or solutions. It can learn from operational data to suggest workflow optimizations, automate complex data analysis, or even generate documentation and compliance reports with much greater detail and accuracy, thereby improving efficiency, reducing errors, and enabling staff to focus on strategic roles.
Navigating the challenges of GenAI implementation
While GenAI offers transformative potential in asset management, it also introduces specific challenges:
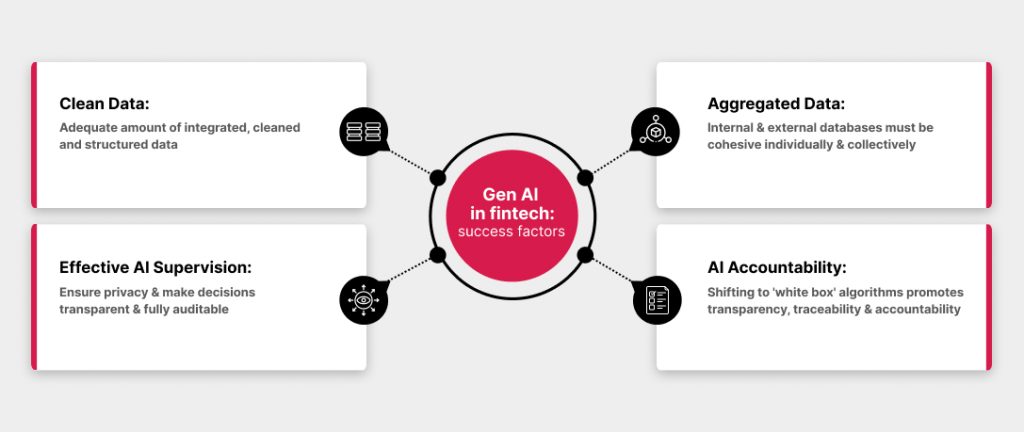
- Ethical and Regulatory Challenges: GenAI’s ability to generate new data or content amplifies concerns about transparency, especially since the decision-making process can be less straightforward than traditional AI. This raises issues about decisions, the potential for bias in generated outputs, and who is accountable for AI-generated actions or recommendations. Ensuring compliance with emerging regulations like the EU AI Act is particularly challenging when dealing with AI that creates rather than just processes data.
- Trust in AI Models: The complexity of GenAI models, which can generate novel insights or scenarios, makes it harder to achieve explainability. Building trust in these systems necessitates more transparent and interpretable models where the logic behind generated data or decisions can be understood. For instance, if a GenAI model suggests a unique investment strategy, investors and regulators need to understand the basis of this recommendation.
- Data Quality and Management: GenAI’s dependence on structured and unstructured data makes data quality critical. Poor data can lead to the generation of misleading or biased insights, potentially causing significant errors in market analysis or investment strategies. Moreover, managing the vast, diverse datasets GenAI uses requires sophisticated systems, and ensuring data privacy under regulations like GDPR becomes more complex when AI can generate new data that might mimic real personal data.
- Skill Gaps and Interdisciplinary Expertise: Integrating GenAI into asset management demands technical AI expertise and an understanding of how to apply these technologies creatively in financial contexts. The unique challenge here is training or hiring professionals who interpret and utilize GenAI’s novel outputs. Bridging this skill gap involves interdisciplinary collaboration, where financial acumen meets advanced data science capabilities, perhaps through initiatives like specialized training or partnerships (e.g., similar to Goldman Sachs’ approach to data accessibility).
What’s next for GenAI in the asset management industry
The future of asset management will be significantly influenced by advancements in GenAI, particularly beyond 2026. Here’s how:
- Advanced Model Capabilities: GenAI will evolve to handle even more complex and large-scale datasets, generating insights and crafting entirely new data points or scenarios more precisely. These models will push the boundaries of predictive analytics, offering unprecedented deep insights into market behaviors and investment opportunities.
- Innovative Investment Strategies: GenAI’s capacity to simulate countless market conditions will lead to the development of novel investment strategies. These strategies could dynamically adjust in real time to market changes, leveraging the technology’s ability to generate and analyze previously unimaginable scenarios.
- Customization at Scale: With GenAI, fully automated investment platforms might emerge, capable of providing hyper-personalized investment plans based on real-time data and individual investor profiles. This personalization will go beyond what current AI offers, tailoring investments to specific client needs, risk tolerances, and preferences.
- Enhanced Human-AI Collaboration: While AI advances, human advisors will continue to play an essential role, particularly in areas requiring intuition, ethical judgment, and nuanced client interactions. The partnership between human advisors and GenAI will deepen, with AI providing data-driven insights and humans offering contextual understanding and relationship management.
- Regulatory Evolution: GenAI’s unique capabilities, especially its ability to generate new data or insights, will likely spur new regulatory frameworks. These will ensure ethical use, transparency, and accountability in finance, focusing on how generated data is used, the explainability of AI decisions, and the prevention of AI-driven market manipulations or biases.
- Global Market Influence: Asia-based hedge funds investing in AI innovation, particularly in China, highlight a trend where regions with advanced AI development will influence global asset management practices. GenAI could become a key differentiator in markets where data is abundant and diverse.
The trajectory of GenAI in asset management points towards a future where investment strategies are not only data-driven but also creatively and dynamically generated. This offers challenges and opportunities regarding regulation, ethics, and human involvement.
Conclusion
GenAI is transforming asset and wealth management; strategic use across key areas like portfolio optimization, risk management, client onboarding, compliance, and personalized insights can unlock efficiency, innovation, and value. However, a well-defined strategy, robust governance, and pragmatic implementation are crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring compliance. Firms successfully navigating this transformation will lead the industry’s digital revolution, but they must always balance technological advancements with irreplaceable human oversight in decision-making.




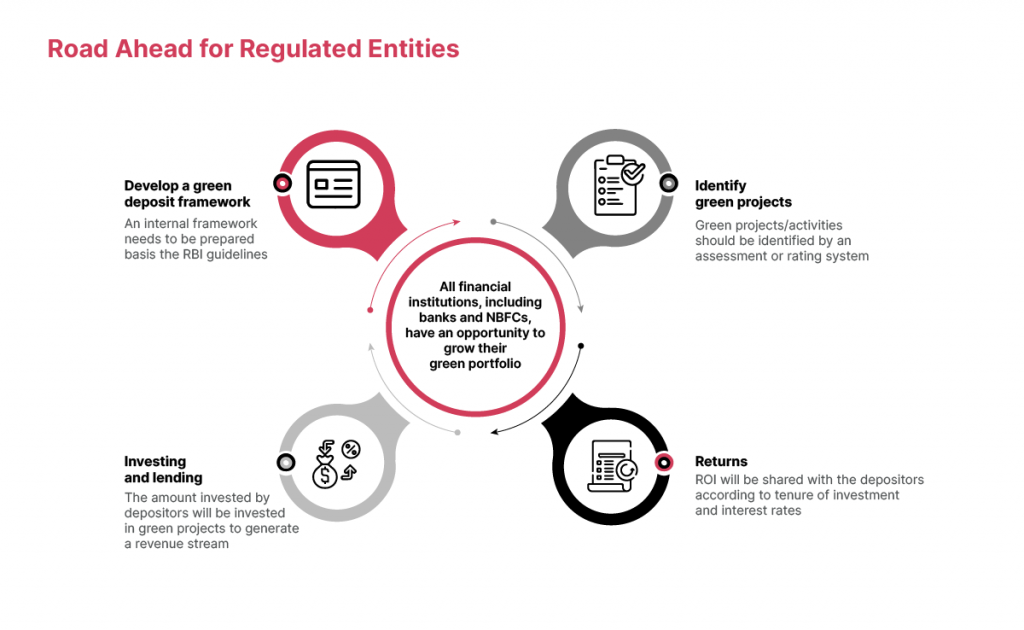
 1. Renewable Energy:
1. Renewable Energy: