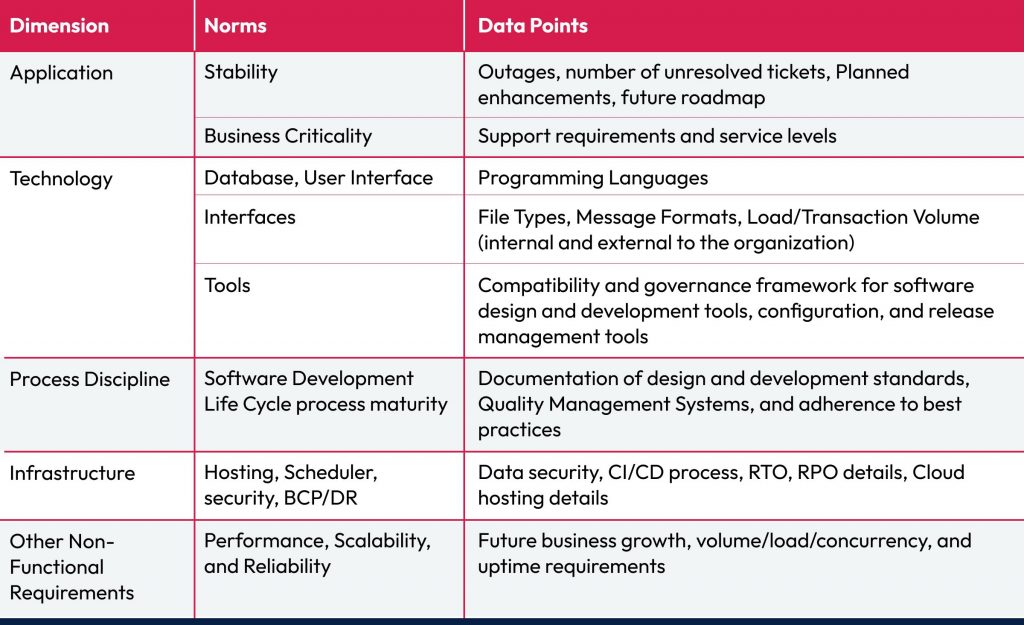
The future of banking lies in seamless connectivity. Banking APIs have emerged as the essential components within the financial services industry, facilitating real-time transactions among various financial applications and services. Behind the scenes, the Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) drive various convenient functionalities such as account management, payment processing, transaction history retrieval, and third-party financial tools. Today, banks collaborate with Fintech and third-party partners using bank APIs, offering personalized financial solutions and adapting to evolving customer needs.
Banks embracing digital transformation rely heavily on APIs to provide innovative financial services. However, with the increased use of APIs come risks and security challenges for banking and financial institutions. As more data is shared through banking APIs, potential data threats and attacks exponentially increase. So, how do we balance innovation in financial services with banking API security? In this article, we have provided insights into 7 key challenges banking institutions face in protecting their APIs and key API security best practices to bolster security posture.
Key challenges in banking API security
As the financial industry continues to shift towards open banking and API-based solutions, some obstacles to the security of these solutions arise. Here are 8 key challenges in open banking API security that banking institutions must address to build secure and customer-centric digital solutions:
- Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
Open banking APIs are interconnected with various applications and services and thus create an expanded attack surface. The vast amount of sensitive customer information transmitted via bank APIs can have open-ended vulnerabilities such as unauthorized access and data breaches. Attackers can exploit even minute vulnerabilities to access sensitive customer information, such as their personal data, credit card details, and account numbers.
- API Endpoint Security
The security of API endpoints is critical to protecting the overall infrastructure. Malicious actors often target vulnerabilities in API endpoints to launch attacks, such as code injection attack attempts.
- Code Injections
On the authentication and validation front, bank APIs must have strong security standards to avoid gaps. Banking institutions cannot afford even the slightest gaps in authentication protocols because such gaps can be vulnerable to code injections by attackers. Using such gaps, attackers may send a script to a banking application’s server via an API request. This may lead to Account Takeover (ATO) incidents and put the application’s internals at risk—it may delete data and plant false information in the application environment.
- Encryption and Data Integrity
The confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted through banking APIs are always at risk of attacks if the encryption protocols are insufficient to safeguard data in transit and at rest.
- Communication Channels
API transactions are facilitated by multiple communication channels between systems and parties that ensure faster transactions. However, these channels can be vulnerable to security threats like data manipulation, eavesdropping, and man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
- Regulatory Compliance
The banking and financial services industry is subject to data regulations like GDPR and PSD2 and security standards such as ISO 27001 to protect customer data and ensure a secure financial landscape. Non-compliance with these standards can result in a more expanded attack surface, severe legal consequences, bank APIs prone to emerging threats, and damage to financial institutions’ reputations.
- Brand Reputation
Security breaches that expose sensitive customer data can systematically erode the hard-earned trust between banks and their clientele. The resulting damage to the institution’s reputation and perceived reliability presents financial and existential risks associated with losing competitive positioning grounded in customer loyalty. Therefore, prioritizing robust banking API security via routine vulnerability assessments and continuous authentication enhancements is an investment in maintaining customer confidence and institutional reputation.
- Fraud Detection
APIs facilitate real-time banking operations and connect banks to external services, such as payment processors or fintech platforms, attracting additional risks by expanding the ecosystem’s threat surface. As a result, APIs can become attractive targets for fraudulent activities—automated attacks, transaction manipulation, identity spoofing, and bypassing transaction limits using legitimate but compromised credentials. Above all, with traditional fraud detection mechanisms, malicious behaviors and real-time API traffic patterns can go undetected, leading to significant financial losses and reputational harm.
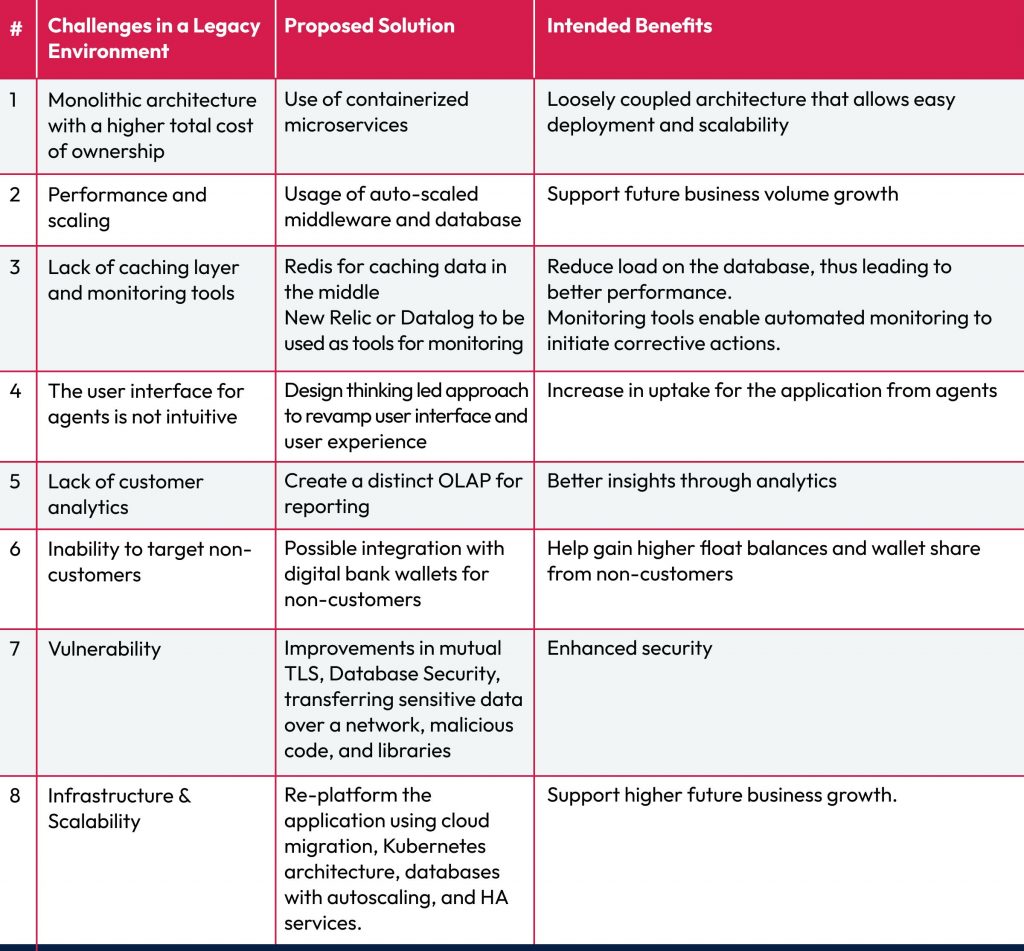
11 strategies for tackling banking API security challenges
Banks must implement a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy covering all security aspects to tackle open banking API security challenges. Here are key banking API security best practices that banks can adopt to enhance their security measures:
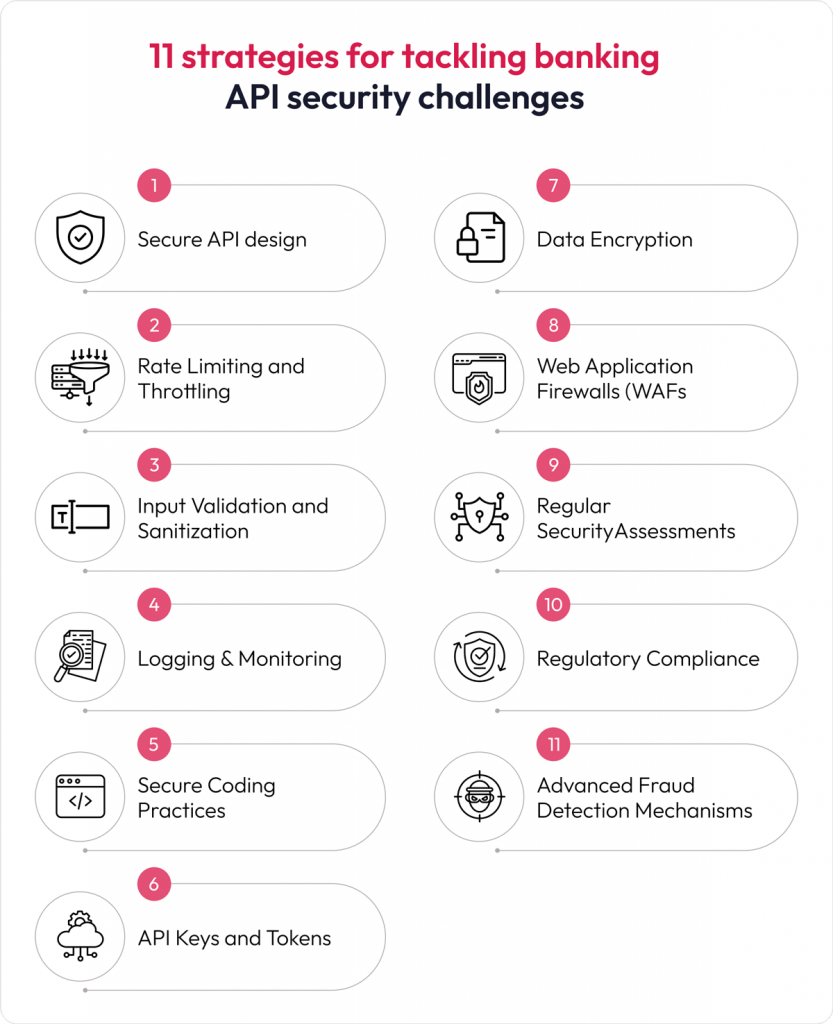
- Secure API Design
Banks can perform exhaustive threat modeling, risk assessments, and attack surface analysis during API design phases. Identify attack vectors like code injection attacks, MITM attacks, bot abuse, etc. They can architect appropriate countermeasures directly into the API framework with principles of least privilege.
- Rate Limiting and Throttling
Banks can implement rate limiting and throttling mechanisms to prevent abuse and protect against distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Set appropriate limits on the number of API requests per client or user within a given timeframe.
- Input Validation and Sanitization
Banking institutions can adopt a Zero-trust model with input validation and sanitization. They can validate and sanitize all inputs to prevent common security vulnerabilities such as injection attacks (e.g., SQL injection, XSS). Use parameterized queries for database interactions and implement input validation for API payloads.
- Logging & Monitoring:
Log all API activities, including requests, responses, and errors, for auditing and forensic purposes. Implement real-time monitoring and alerting to promptly detect and respond to suspicious activities or security incidents.
- Secure Coding Practices
Financial institutions can adopt DevSecOps methods with extensive security testing integrated at each API development stage. They can enforce robust coding standards, including proper input validation, data sanitization, and parameterized queries. This protects against common web application security threats like cross-site scripting (XSS) and cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
- API Keys and Tokens
Banks can employ issuing unique API keys or tokens to each authorized client to authenticate their requests. Use short-lived tokens and implement token expiration and refresh mechanisms to mitigate the risk of token misuse.
- Data Encryption
Employ strong encryption algorithms to encrypt sensitive data end-to-end using standards like AES-256. Banks can implement hashing algorithms like SHA-2 on sensitive data in transit and at rest and apply digital signatures to ensure data integrity. These practices can anonymize or mask any Personally Identifiable Information (PII) data that flows as needed per data privacy regulations.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAFs)
Banks can deploy advanced web application firewalls (WAFs) to analyze and filter real-time API traffic. Fine-tuned WAF policies using signatures, anomaly detection, and behavioral analysis can detect and block common attacks like code injection attempts, bot abuse, and DDoS floods.
- Regular Security Assessments
Frequent security assessments are crucial to identify vulnerabilities before exploitation by cyber-attackers. Banks must conduct recurring penetration tests, static or dynamic scans, and code audits performed by internal and third-party security teams. This allows the discovery and remediation of flaws like code injection risks, weak authentication, and misconfigurations.
- Regulatory Compliance
Banks must maintain compliance with data regulations like GDPR and security standards such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF) and ISO 27001 to keep bank APIs resilient to emerging threats.
- Advanced Fraud Detection Mechanisms
Banks must integrate advanced behavioral analytics and implement AI-driven anomaly detection systems to monitor API traffic in real time for unusual behavioral patterns—such as transaction volumes, unusual login behavior, and device mismatches. Advanced fraud detection mechanisms can be embedded directly into API gateway or backend infrastructure, using risk scoring models to flag suspicious activity and detect anomalies before the financial loss occurs—without degrading user experience.
The banking API security imperative
Maintaining stringent banking API security measures is paramount as the banking industry continues to embrace API-driven platforms. Financial institutions can accelerate their digital transformation by utilizing banking APIs while also being vigilant to ensure a robust security posture. By taking the necessary secure API development measures, banks can reinforce customer trust, system resilience, and reputation as stewards of sensitive financial data.
Ultimately, API connectivity promises greater convenience, personalized services, and streamlined banking. However, banking institutions can only achieve this on a foundation of security and compliance first by following banking API security best practices. At Robosoft, we partner with leading banking and financial services organizations across the globe, enabling them to streamline operations and provide millions of customers with secure and seamless digital experiences.






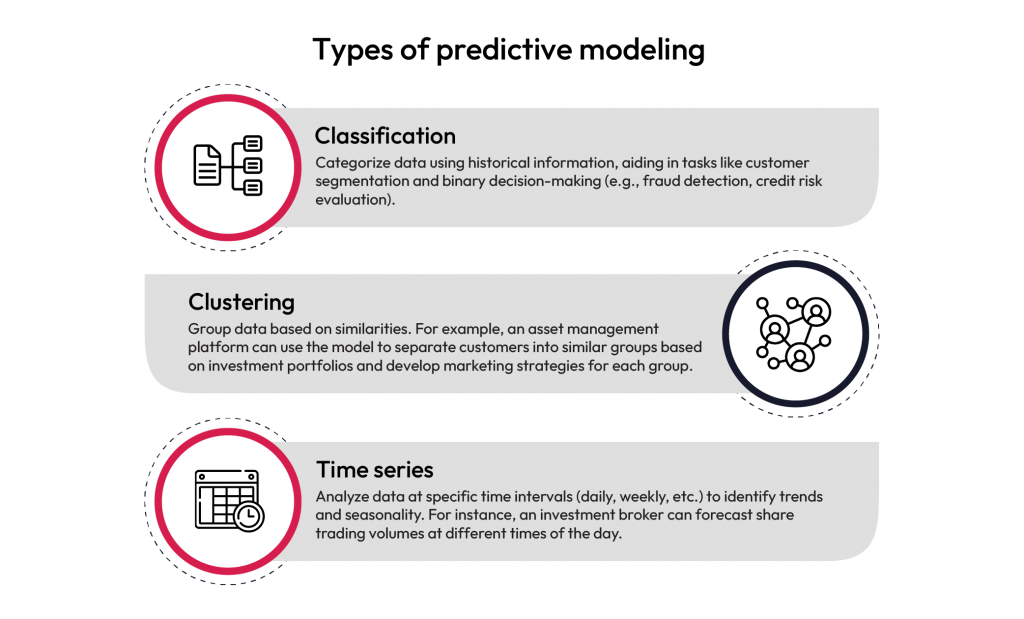
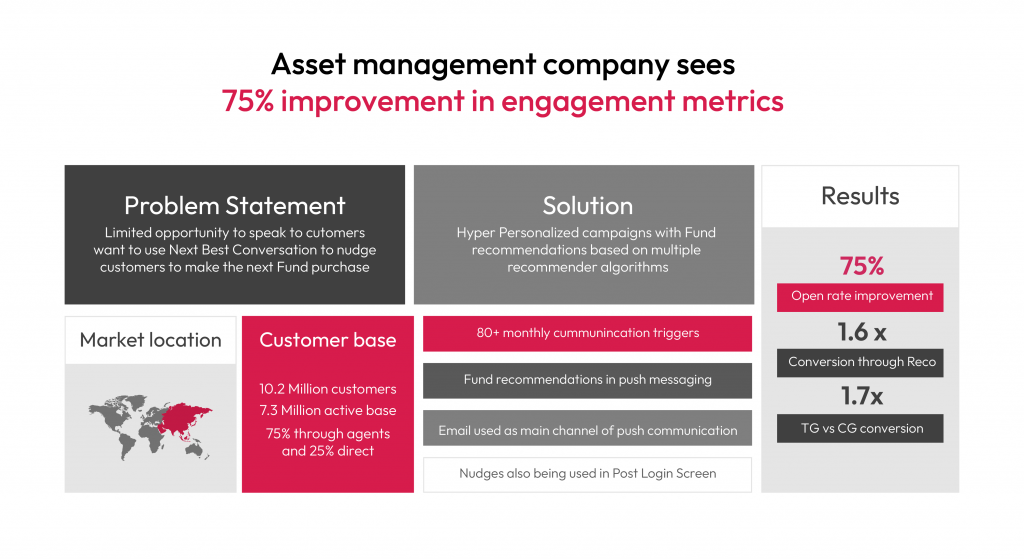

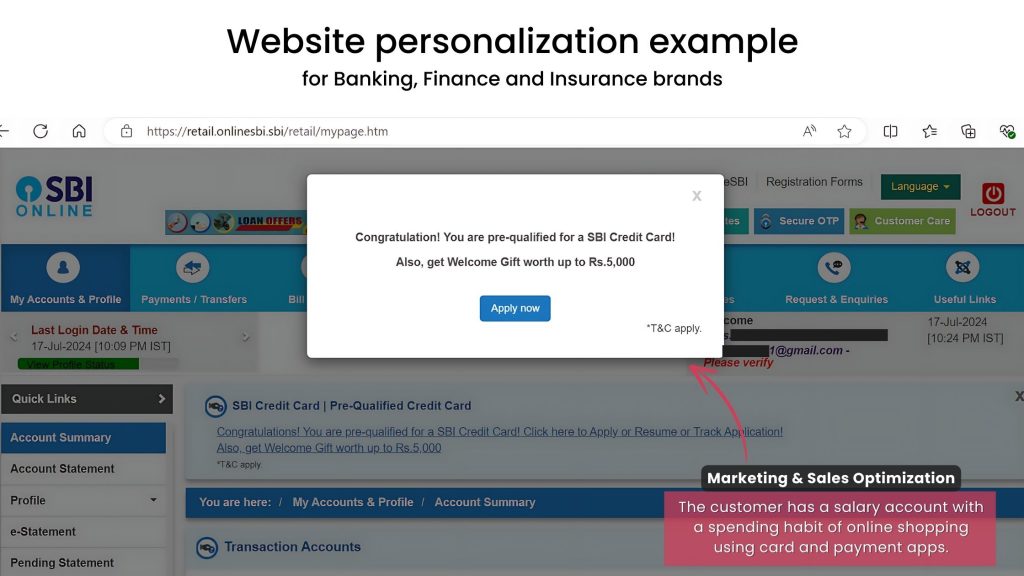
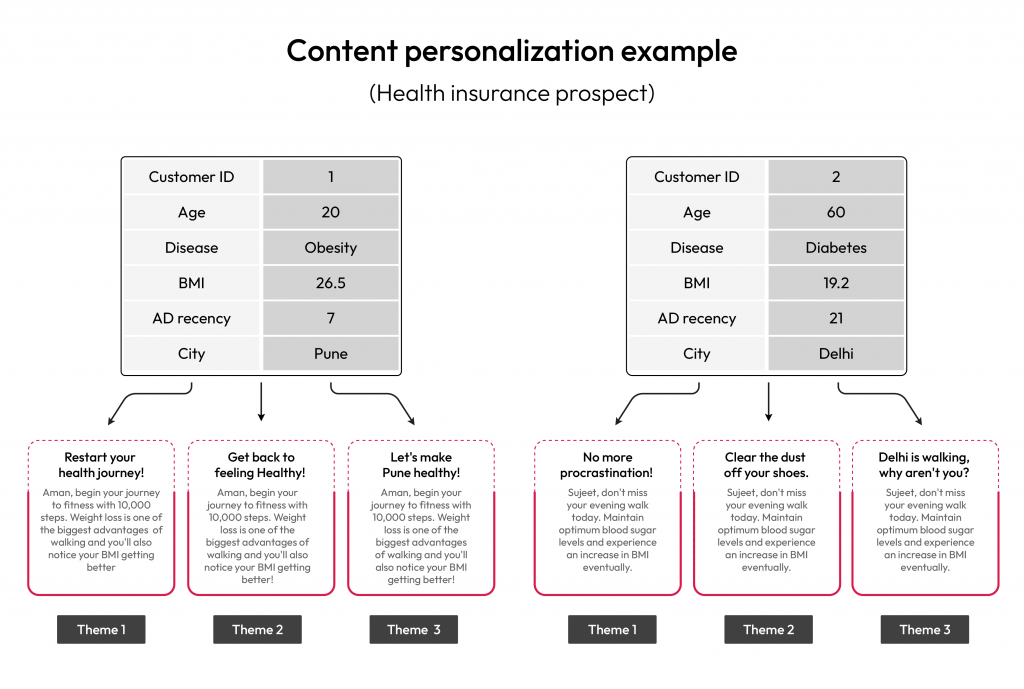





 1. Renewable Energy:
1. Renewable Energy: