Since the dawn of time, pursuing their significant other has always been one of the life purposes of a living being. Be it humans, animals, birds, or mammals, all go through this natural order of mate selection to populate their species. While animals and birds and others usually fight it out to present themselves as the strongest candidate, things have become much easier in the case of humans – all thanks to technology and dating apps.
Cavemen and medieval men used to fight and duel over the approval of a woman. Nowadays a quirky bio and just a right swipe is enough.
The 90s saw a rise of matchmaking websites in India as well as globally with shaadi.com, bharatmatrimony.com, match.com, and others. They started out as preferred online medium to find suitable matches according to social compatibility like caste, culture, region, language education, etc. But very much like Netflix took over Napster, Tinder’s mobile first platform-based approach took over existing linear based models to become the popular choice of dating medium. Globally, Tinder was the highest grossing non-gaming app in 2017.
The online dating market showed no signs of slowing down during and after the pandemic and have been valued at US$12.37 billion in 2021. It is now expected to be worth US$28.36 billion by 2027. We are seeing an influx of dating apps such as Bumble, Hinge, Grindr, Hily, Clover, Plenty of Fish, etc. They all come with their own unique proposition of finding matches for their users. As the dating behaviors of users change with time, these apps adapt to these changes and provide what their users need.
Trend is in the app
Trends are nothing but a general direction of change in something. The biggest transition we can see in the dating scenario is that now people are being more selective of who they go out with.
A recent survey shows “61% of daters use an online dating app to meet people that shares common interests, 44% of daters use an online dating app to meet someone who shares their values and beliefs, and 42% of daters use an online dating app to meet someone for marriage”.
These numbers indicate the current mindset of people regarding their partner selection by the dating app.
The pandemic caused a lot of mental, emotional, and physical stress upon people. As a result, people had more time to reflect on their needs and priorities. The dating apps acknowledged their users’ priorities and introduced several technology-driven features to heed their needs. Below are some of the noticeable CX and behavioral trends among daters and dating apps-
#1 Let’s take it slow
While the pandemic forced people to stay inside, the dating apps didn’t suffer its consequences. In fact, research by Sensor Tower shows that dating app downloads grew 3% Y/Y in Q4 of 2020. The same research also indicates the average age for dating apps has steadily declined in recent years. The declining average age was more visible from the Q1 to Q3 of 2020.
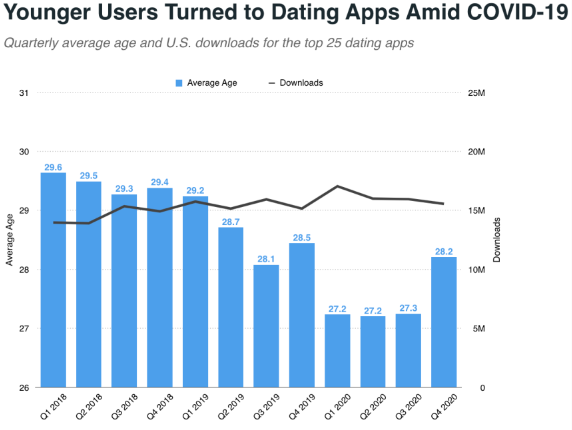
Source: Sensor Tower
There are new dating terms that are making the rounds among young users from millennials and Gen Z – Dry Dating, Hesidating, Slow Dating. All terms coined due to the unwillingness of people to go all out with complete strangers.
According to Tinder’s CEO, Renate Nyborg, Gen Z consists of more than half its user base and they eventually want to take things slow in dating. Their idea of ideal dating scenario is different from millennials as they want to know their potential matches better before committing themselves romantically or meeting them. Tinder launched different intent-based swipe features for its users. They can now match by adding “Passions, Prompts and Vibes” to their respective profiles. All things helping matches to know each other better without any romantic expectations and then only take things further if “vibes match”.
#2 Discretion for safety reasons
Dating apps leveraged their digital capabilities to remain competitive in the times of full lockdown. As in-person meetings were not possible then, dating apps introduced in-app video call features for locked-in individuals. The nimbleness of dating apps to adopt to a change was one of the reasons their demand didn’t go down like other businesses.
But as people are using the video call features more and more, it raises the question of privacy and safety. This resulted in many dating apps now offering discreet video call features where users can video call with their blurred faces or silhouettes. The new video call feature also takes user’s permissions before connecting a call for increased discretion. Due to heightened safety concerns, many dating apps started taking different measures to address those. S’More defines itself as an “anti-superficial dating app” as it doesn’t straightaway reveal the image of its users. The profile image appears as blur initially and gets clearer as the conversation continues between matches.
#3 Minimal efforts maximum gain
Almost all the freemium dating apps like Tinder offer a limited number of free swipes per day to their users. However, the introduction of AI based recommendations has increased the likelihood of users being hooked to the app. AI and ML learn from user’s personal data and preferences to ensure every match has the possibility to be “the one”.
There are over 300 million dating app users worldwide with about 20 million subscribed to one of their premium features. It creates an opportunity for dating apps to increase the likelihood of in-app purchases by offering more value or better matches to their users.
#4 Inclusivity for exclusivity
The huge popularity of value-driven, niche dating platforms in recent years have indicated a change from mindless swiping by global users. People now prefer quality over quantity and are looking for dating apps where they “truly belong”. There are already successful apps like Grindr catering to gay, bisexual and bi-curious men. Similarly, there are other niche dating apps that cater to either sexual preferences, hobbies, or interests of users.
Dig – for dog lovers is a niche dating app consisting of only dog loving users. It totally eliminates the concern of daters about what their match would think about their favorite pet.
Veggly is a dating app specifically for vegans and vegetarians.
Tastebuds is especially built for music lovers who match and can immediately start discussing their favorite artists, bands, etc.
BLK is a dating app for Black singles in the black community. It strives to create a warm, inviting, supportive, and inclusive space where Black love is celebrated and respected in all its forms.
Her dating app is specially built for lesbian, bi and queer community. The free version of the app lets you add friends, view profiles, start chats, view events, and join communities.
Other popular apps like Tinder, Hinge, Bumble have taken cues from this and redesigned their apps to included more sex orientation selections, more varied interests, suggestive bios to showcase on a profile.
#5 It’s a social thing now
One of the most difficult steps in online dating is the talking phase where you try to find common things to talk about. That’s when you feel the need for a friend to support you and guide you. Dating apps like Fourplay encourage people to form a tag team and team up with two more as they start messaging each other.
Thursday app helps skip the talking phase altogether and brings the online dating community directly offline. It hosts secret parties where only singles are allowed. The most likely scenario is a person would be taking along one of their single friends to these events and “socialize”. Ship (now discontinued) allowed users to become a matchmaker and find a suitable match for their friend. It also offered a group chat feature for better validation of the potential match.
#6 Gamification could be the key
Tinder’s “Swipe Night” was a huge success. It allows the user to solve a mystery based on game narration and first-person adventure. User’s choices allow to dictate the story and reveal different answers based on that. It then allows users to highlight their game answers in their respective Tinder bios. They are more likely to match with people who have similar answers and thinking patterns
Bumble introduced sets of recommended ice breaking questions to help matches get over the initial nervousness and start talking. Both users answer one of the chosen ice breaking questions and match their answers. Based on the answers they can carry forward their conversation.
Technology – the ultimate matchmaker in the digital era
Dating apps are indeed tech companies leveraging technology to offer social values. The fast adoption of newer technologies and digital transformation in every industry can be seen in dating apps as well. Dating apps are now taking advantage of cutting-edge software and technology such as AI/ML, VR, Metaverse to provide a whole new experience in dating to its users. Let’s take a deeper look at how these technologies are playing a matchmaking role in our dating lives –
AI/ML
Earlier Tinder used an ELO algorithm for matching profiles on the platform. It worked on a weightage system where users with most right swipes had a better probability of finding matches quicker. It then now moved away from this and now relies on a “dynamic system” that monitors the user behaviors on the platform through their swiping patterns and what’s on their profiles. Although not mentioned clearly, this dynamic system could be all but AI and ML deployed by Tinder for matching profiles.
“In a recent interview, Jennifer Flashman – Tinder’s director of analytics, explains that in leveraging AI to build better user experiences, it’s become clear to her that the future of dating will increasingly occur over texts and DMs rather than blind dates and phone calls. As this shift continues to accelerate, here are the top reasons she thinks companies are “swiping right” on AI in dating—and why other industries should be figuring out how to swipe right!”
AI and ML are already creating efficient and smart business processes in different industries. It has potential to transform the dating industry as well. The dating app Hinge employs machine learning as part of its algorithm by suggesting a “Most Compatible” match to its users.
5G
5G with its increased bandwidth, reliability, and speed has made it possible for dating apps to introduce more video-based features in their apps. Although the main beneficiary of 5G services is the OTT industry. But dating apps also can enjoy a few benefits of 5G. Dating apps now offer buffer-less video call, uninterrupted live streaming, Netflix party, etc. to their users for increased engagement. With time we can only imagine other benefits 5G and its subsequent updates may bring to the dating world.
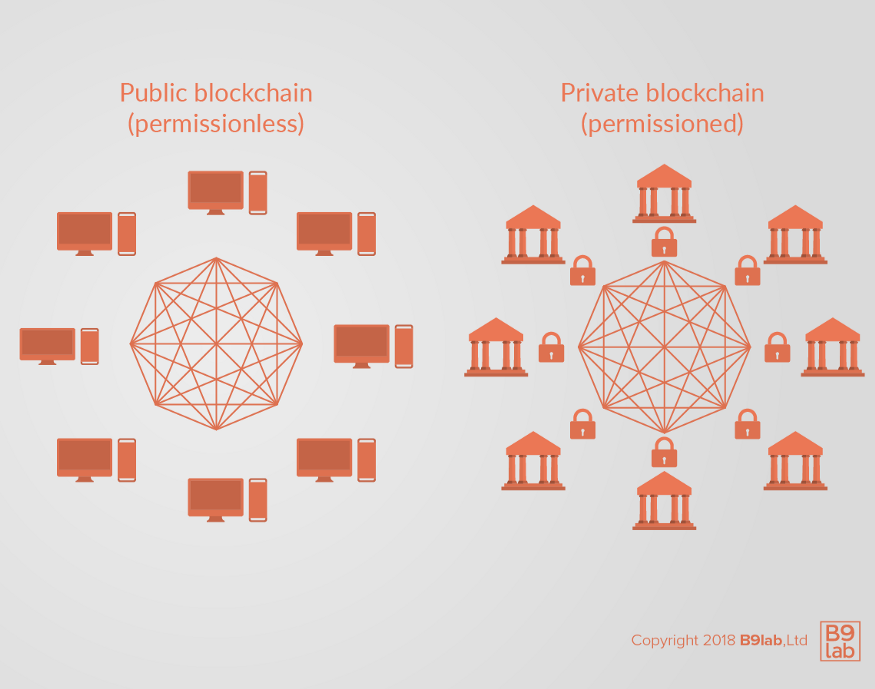
Blockchain
The two founding principles of blockchain are full transparency and immutability. These two factors can play a major role in verifying user identities in dating apps while maintaining the option of privacy.
German company Hicky was one of the first to introduce blockchain based dating app back in 2018. It was built to ensure security and incentivize good behavior of its users.
Luna works on a tokenized dating system and incentivizes people to choose their contacts more carefully.
Ponder uses blockchain-based recommendation system and game mechanics in its app. It also offers financial rewards to motivate everyone to play matchmaker for their friends.
VR and Metaverse
The possibilities of Metaverse are endless for daters. It opens the gate to a whole new world of possibilities for them. Dating in metaverse framework depends on the idea of avatars, an advanced articulation of an individual. Nevermet strives to find matches for people in the Metaverse and VR. Dating applications with a metaverse framework depend on the idea of avatars, an advanced articulation of an individual.
Read more: Metaverse or MetaAverse – A Design Thinking Approach To Future Digital Ecosystems
Finding meaningful relationships in virtual platforms like online gaming is nothing new. But VR dating apps like Flirtual and Planet Theta provide the feeling of being physically present with others as well as bring a significant portion of body language into the mix.
VR technology enables the users to connect with their matches authentically in fantastical environments that are impossible to replicate in the real world. People can visit any location, go to any bar, play with unicorns, all on their first date.
Find your ‘lobster’
Contrary to popular beliefs, it’s the nerds that get the dates. Quite literally!
Being tech companies first, the top dating apps are always in an advantageous position to pivot and redefine their value proposition. They continuously vie for users’ attention and roll out new features whenever deemed necessary. Bumble and Hinge rolled out their new voice prompts while Tinder is working on a social mode called Swipe Party. Bumble also recently had its first acquisition in Fruitz – described promptly as a “Gen Z dating app”.
There is still a large untapped market out there waiting for something in their niche. Currently we have over 1500 dating apps or websites worldwide and with new apps quickly emerging, nothing is certain for established big players. There are plenty of fish in the sea if you have the right strategy in place to catch them. The dating industry is facing a real need to embrace innovation or get overshadowed by newer dating apps with fresher ideas and newer technology behind them. Dating apps have the impetus to improve their transparency and provide users with a more complete experience.