According to a recent report, digitally matured organizations are those who take the road less traveled i.e. their business processes are different than the majority. However, doing things differently is not enough, planning and implementing things differently is the key to success.
Most prudent companies realize how important it is to have a focused and customized digital strategy to excel in a connected world; thereby most digitally matured organizations have a well defined digital strategy in place.
Before embarking on this journey, assessing the organization’s digital maturity will help enterprises in analyzing where to start their digital transformation journey and how to go about creating a ‘digital roadmap’ for the future.
How can organizations start assessing their digital maturity?
Which are the areas to focus on while creating a digital transformation plan?
These are some of the critical questions that we as a digital advisory can help you answer. The right digital partner can help organizations visualize, mobilize and realize their digital transformation strategy.
What does this imply?
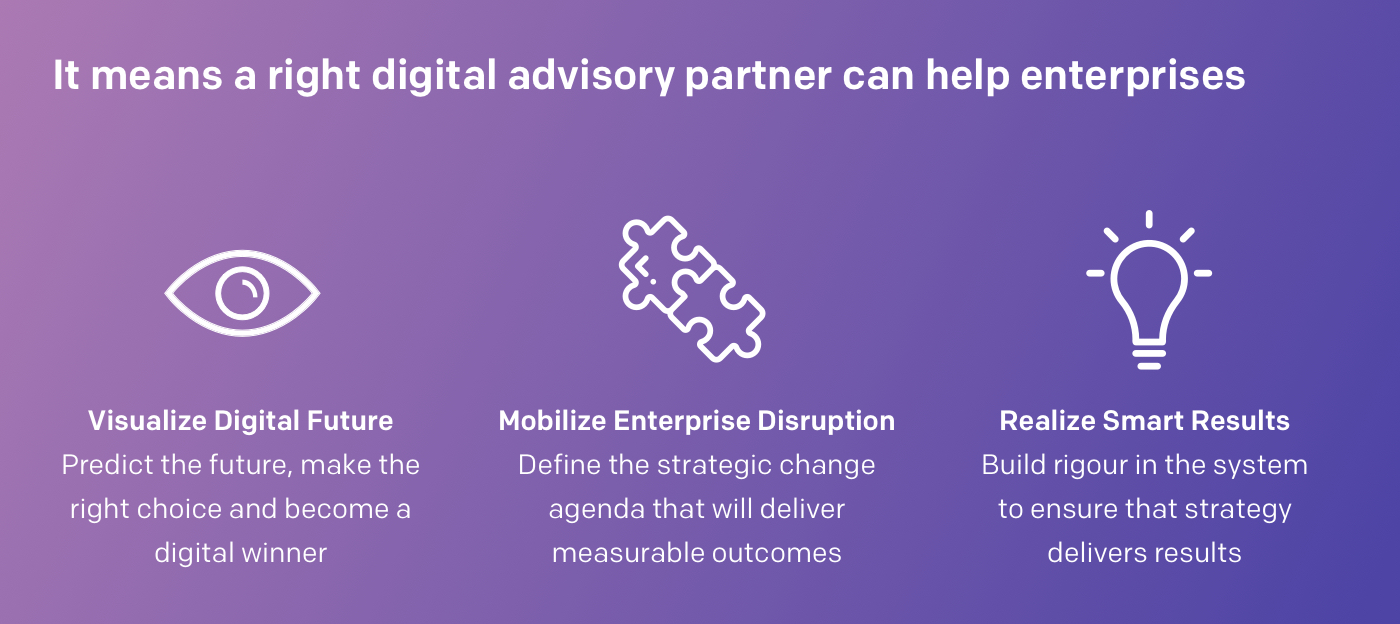
So, where do organizations take the first leap of visualizing their digital future?
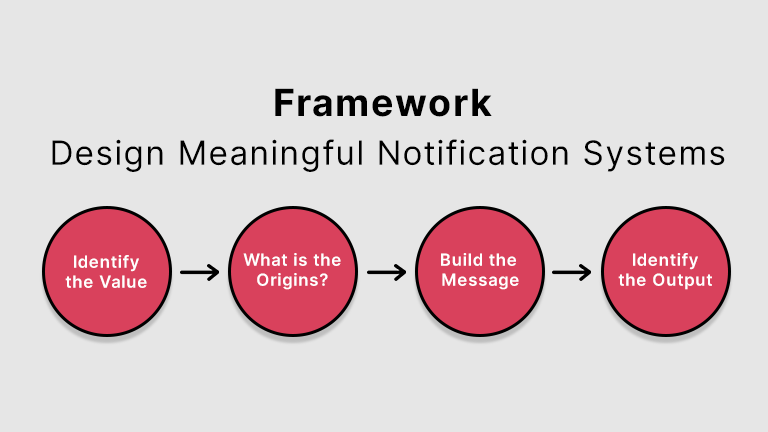
At Robosoft, we follow a 5As framework to help find some truly comprehensive solutions that can scale an organization’s digital journey.
The 5 A’s framework – Access, Autonomy, Alliance, Agility and Algorithms
Digital Maturity Assessment – Using 5 A’s Framework
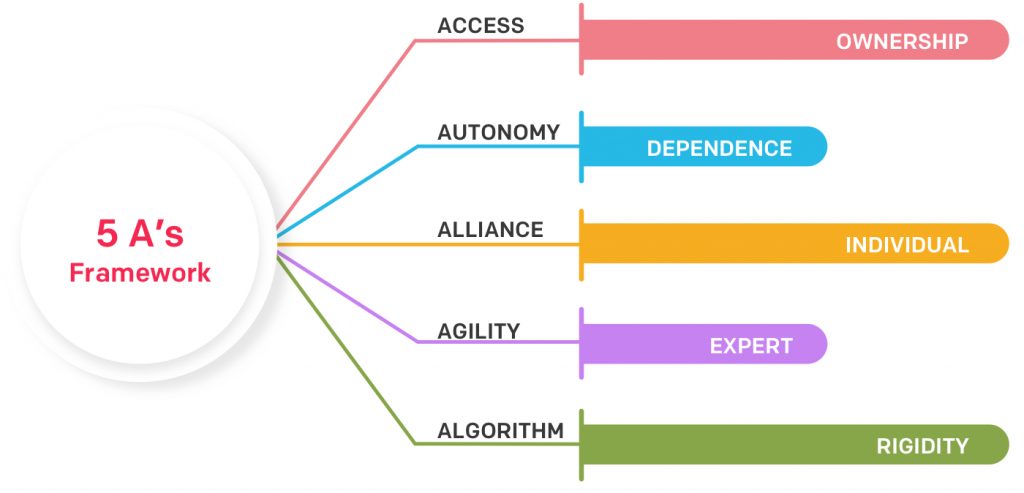
Let’s delve deeper into each of these dimensions.
Access
Today millennials desire access over ownership. With a change in consumer behavior we are rapidly moving towards an access economy.
Access economy is the one where resources are shared – tangible or intangible both – it may mean sharing of the workforce, workspace or even knowledge sharing. With this shift businesses too are imbibing processes and technologies to adapt to an access economy.
What does this mean for enterprises?
- Collaborative working ecosystems
- Optimal usage of resources
- Faster processes
The mantra is ‘value unused is waste’ and that represents a shift in cultural consciousness towards valuing experiences rather than goods. Uber the world’s largest taxi services own no vehicles, Airbnb owns no real estate, Alibaba has no inventory, the advent of sharing or access economy has truly changed the rules of the game.
Here are a few examples of organizations across industries leveraging the access economy-
- Mahindra has recently invested in 2 start-ups Trringo and Smartshift. Trringo is an online platform that gives farmers pay-per-use access to expensive farming equipment. Smartshift is a load exchange platform that connects small commercial vehicle owners with people looking to transport their goods within the city.
- With the dual goal of reducing vacant warehouse space and reaching customers in a new way across mainland Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, DHL Supply Chain has pioneered a platform called DHL Spaces to broker unused warehouse space.
Access economy helps is improving the efficiency of resources and optimizing their usage to increase productivity. Co-working spaces companies like WeWork are helping enterprises optimize their fixed space costs and platforms like Upwork are helping organizations in hiring resources as per the need.
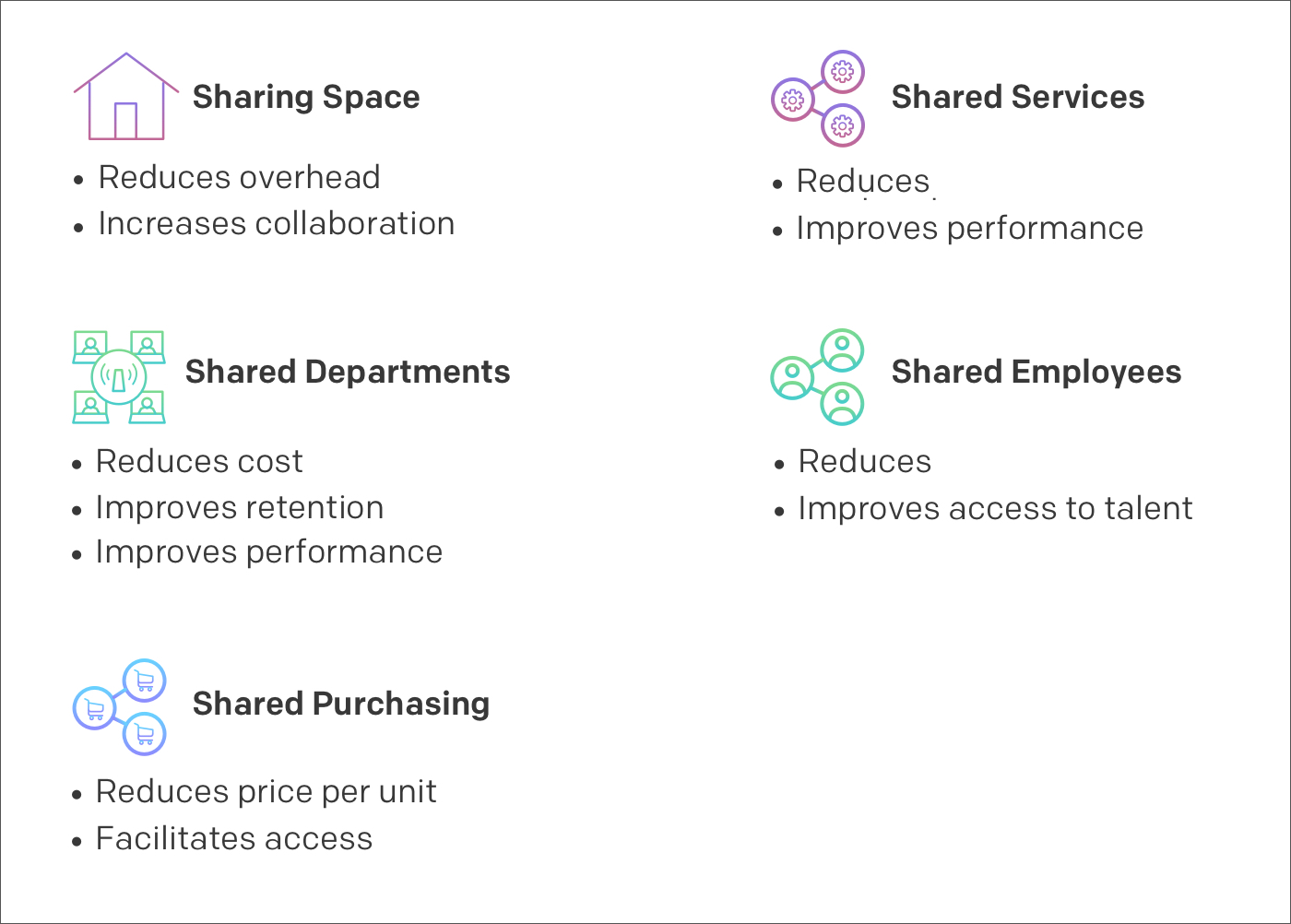
Image source
Autonomy
In a digital economy, consumers seek customization alongside flexibility and autonomy. They like making informed decisions with all the information about a product or service, available on the digital platform. It is thereby upon enterprises to leverage digital media to empower consumers in making more informed choices.
While consumers prefer autonomy, they do not want to lose human contact entirely. They reach out to consumer groups for advice and seek assistance before and after a purchase. The need for the human element is also pushing enterprises to custom-build their bots via technologies like machine learning, AI, NLP, etc.
So how can organizations empower their customers at every step of the customer journey?
- Pre-sales
As per this excerpt, 57% of a sale is made even before the actual purchase. It’s thereby crucial for enterprises to ensure their presence on the right digital platforms at the right time, with essential information about their key offerings.
- Sales
Consumers expect convenient & faster services. This is one of the reasons why e-commerce growth has rapidly scaled in the past few years. Even at physical touch points enterprises are offering options for self-service. For instance, McDonald’s has introduced kiosks at their outlets for consumers to order & receive their food much faster.
- Post-sales
In a self-service economy, customers turn to other customers for feedback, reach out to groups and seek assistance with a faulty product or service. Chatbots help in addressing their grievances in real-time.
However, autonomy is not something that is only desired by customers, but it is sought by employees as well. When it comes to creating a digitally matured organization, creating autonomous processes across stakeholders – internal and external is the key.
Alliance
‘If you want to go fast, go alone. If you want to go far, go together.’
Today economy collaboration has become a critical factor for success. Here are some examples of collaborations that are thrusting the business ecosystem way ahead.
- Home Depot, is working with manufacturers to ensure that the connected home products it sells are compatible with the Wink connected home system, thereby creating its own connected home ecosystem, with a wide range of services that are easy to install.
- Philips’ healthcare practice is collaborating with Salesforce to build a platform that they believe will reshape and optimize the way healthcare is delivered. The platform will create an ecosystem of developers, building healthcare applications to enable collaboration and workflow between doctors and patients across the entire spectrum of care, from self-care and prevention to diagnosis and treatment through recovery and wellness.
The norms of competition to have changed drastically. Netflix is a competitor for Inox, Uber is a competitor for automotive companies, so on and so forth. Businesses will have to move beyond the traditional industry silos and build well-collaborated ecosystems, creating new opportunities for innovation. However, every business will need to team up with other players; competition or outside the industry, basis what their core objectives are. Identifying what kind of collaborations and to what extent is the key to developing a robust digital strategy.
Agility
An agile approach is not just limited to software development. It’s an integral part of every business. In the broadest sense, agility refers to an enterprise having an operational structure that gives it the tools to react quickly and efficiently to the ebb and flow of your market. To achieve this type of responsiveness, you need a huge degree of adaptability and flexibility at every level of your organization.
Fast moving, flexible and robust firm capable of rapid response to unexpected challenges, events and opportunities. Built on policies and processes that facilitate speed and change, it aims to achieve continuous competitive advantage in serving its customers. Agile enterprises use diffused authority and flat organizational structure to speed up information flows among different departments and develop close, trust-based relationships with their customers and suppliers.
An agile business model should be all-encompassing. The IT architecture needs to be adaptable and transformative to respond to market trends as they occur. Internal teams need to operate on an almost ad hoc basis if need be, without being bogged down by outdated hierarchical structures and poor digital tools that only slow down operational responsiveness.
Becoming agile is more about adopting a mindset that determines how people work across every aspect of the business.
To deploy an agile system, organizations will have to alter their operating model. For instance, software firms do not go about launching a full-blown product, rather they create an MVP, which allows them to test, experiment and improve, more often and faster. When it comes to adopting an agile system, it encompasses three aspects of the business – Decision making, Learning & Processes.
Algorithms
In a digital economy, data is the new oil. However, as pointed out in this Forbes article “data inherently is dumb”. So, data alone isn’t enough, we need to enhance it to make the most of it. And, thereby algorithms have become more important than ever. We need algorithms to analyze and bring relevant insights from data to the forefront. And, this is how business leaders will be able to identify specific areas to address.
The Airline industry has been using algorithms to set their passenger fares for ages now. There are a lot of variables that come into picture when setting airline prices like class, the position of seat in the aircraft, the rate at which the tickets are being booked, the time of the year, etc. The yield management program used by the industry constantly monitors supply and demand to get the highest revenue for a given seat inventory. E-commerce websites such as Amazon and Alibaba use the algorithmic business model, mainly for pricing, inventory and seller matching.
However, the level of advancement of an algorithm and the degree to which an organization should invest in algorithms will depend on their industry, business objectives and where they are in their digital journey.
Conclusion
When it comes to creating a digital strategy the ‘one size fits all’ approach doesn’t work. Every organization will have its trajectory while going digital. However, where your organization stands when it comes to the 5As as mentioned in this article will be a critical aspect of defining the journey ahead.

 Image
Image