Are clunky, siloed processes holding your company back? Reimagining your business workflows with SAP Signavio can unlock a world of benefits. While helpful for basic visualization, traditional tools like Visio and flowcharts often lack the collaborative features and data-driven insights needed for true process optimization. SAP Signavio goes beyond simple diagramming to truly streamline operations, eliminate bottlenecks, and empower your business to become a lean, competitive machine.
SAP Signavio is a powerful suite of business process transformation tools designed to help organizations achieve process excellence and drive efforts to effective business process transformation in a comprehensive, intuitive, and data-driven way. In this blog, we’ll look at SAP Signavio’s business process management solution, providing a complete cloud-based modeling platform that makes it easier for you to standardize processes, fix inefficiencies, improve productivity, and achieve business outcomes.
Why does your business need SAP Signavio’s business process management suite?
At the core of SAP Signavio’s offering is SAP Signavio Process Manager, which enables you to realize business process management goals. It provides a long-term competitive edge by allowing organizations to adapt their processes continuously rather than implementing changes just once. It enables your team to:
- Increase efficiency by lowering costs and streamlining processes
- Implement new business concepts or reorganize company lines
- Promote innovation and speed to market
- Enhance customer experience to increase loyalty
- Standardize operations and align teams
SAP Signavio support in S/4HANA transformation projects
The SAP Signavio methodology is designed specifically to provide an end-to-end approach to business process transformation for SAP S/4HANA transformation projects. It addresses several integration aspects, including the integration with Application Lifecycle Management. All actions related to the analysis, design, and enhancement of business processes are the main focus. The tasks are divided into crucial phases like process analysis, design, and enablement.
The switch to SAP S/4HANA is “just” one significant process transformation milestone, and there will be many more as business demands change. By using data-driven insights to expedite the SAP Activate processes and digitalize the outcomes, organizations can lay the foundation for a continuous improvement process.
What are the features of SAP Signavio?
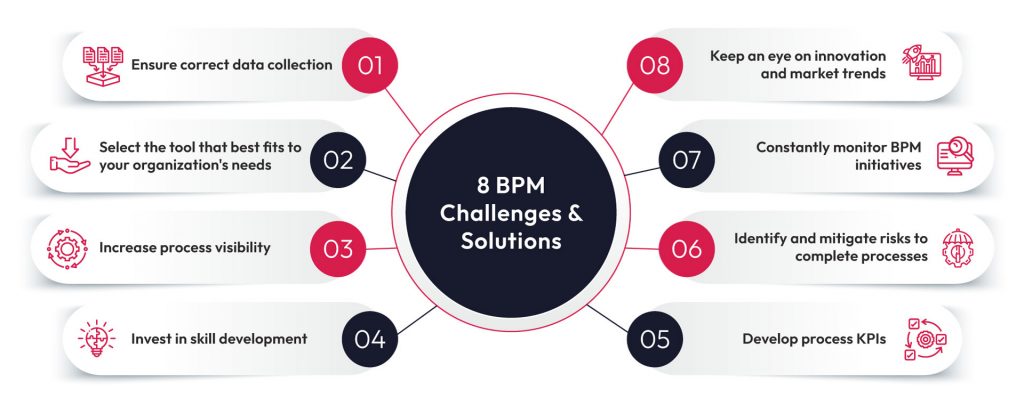
In our blog, Business Process Modeling with SAP Signavio, we have covered how to model the process flows and the key functions of SAP Signavio. But just modeling isn’t enough. You need to manage the process, too. Its feature set includes capabilities for business process management, analysis, documentation, and execution, making it a valuable asset for businesses seeking to drive process efficiency.
Business Process Management
Business Process Management (BPM) is a systematic approach to optimizing and managing business processes within your organization. BPM allows you to complete tasks more efficiently. Most firms have departments that are still focused on themselves. However, they must gain an understanding of what else is going on in their organization or what is required of a specific function. End-to-end thinking is wishful thinking, and by recognizing this, your business will gain a lot from BPM.
Business process management integrates IT, business processes, and people. Here are its benefits:
- One centralized source of truth in your organization
- BPM promotes end-to-end thinking within the organization and communication among divisions
- Critical judgments are more objectively supported by utilizing process data
- More transparency about duties and responsibilities
- A comprehensive analysis of the impact of digital transformation
Process Documentation
Each organization has its own business processes, as does yours. Do you want to expand by optimizing and standardizing them? First and foremost, you must start by understanding your current situation and correctly documenting your processes.
- How do you do what you do?
- Which processes are you affecting, and who or what is affected?
- As-is process documentation is an important first step toward improving your business. But how do you tackle it in an organized way?
By capturing the as-is processes around these interfaces in a BPM tool, you may increase transparency regarding roles, activities, risks, and integrations. This enables you to create a digital blueprint for your firm and briefly shows you where the bottlenecks in your end-to-end processes are. What are the next steps? Develop, implement, and analyze. However, it all begins with accurate as-is process documentation.
Documenting processes is simple using SAP Signavio. To make things even easier, the Process Explorer already includes standard material. However, SAP best-practice processes are also included.
Process Design
When an organization experiences a transition, it is essential to reassess and modify existing business processes as needed. Before you can do anything else, you must first determine your destination. What does the desired outcome look like? Who’s involved? What documents should be delivered? And what kind of approbation are you looking for? The to-be process in the process design phase provides a clear picture.
Your as-is processes are the starting point. Following that, you begin working to decide where you want to go. To future-proof your organization and processes, bring together the right people. Workshops provide insights into obstacles and potential for change.
Now that you’ve covered the fundamentals compare the existing condition (as-is) to the future procedure. After all, how do you ensure an efficient transition? And that all stakeholders be engaged and trained. Furthermore, you objectively compare the current and future situations to estimate the extent of change. This can be done manually, but SAP Signavio also provides a standard comparison model for it. Your new process is in place. But that’s mostly on paper. SAP’s best practices help you go a step further. You can use them to compare SAP with the as-is situation.
Process Implementation
When new processes have been designed, and all stakeholders have agreed to a new way of working, you can put them into action. The implementation phase covers all necessary activities to ensure the solution succeeds in your organization. Process Implementation can only succeed if everyone uses the new tool. SAP Signavio enables you to do just that.
Some processes are virtually the same across multiple firms. This is why SAP created best practices for each standard process. These best practices combine the components of process, system, and organization to create an optimal standard. A fit-to-standard approach eliminates the need for customization. As a result, solutions may be deployed quicker, and new functions can be used sooner.
SAP Signavio is the ideal tool to guide fit-to-standard workshops and validate to-be processes. With Signavio, you make the impact on people and organizations transparent and let the transition take place in a controlled way.
Process Analysis
You’ve planned out your present process, decided where you want to go, and successfully implemented it. That would seem to complete the circle. But this could not be further from the truth. Because how will you know whether the installation was successful? Are all processes followed? And how much is truly saved? You can only answer these questions with a thorough analysis.
Data is essential for gaining deeper insight into your processes and setting KPIs. However, it is analysis that enables you to design your procedures more effectively.
To keep moving forward, you must remain focused on your procedures and continually evaluate them. The first step is to monitor your business actions on a continuous basis. This provides immediate visual insight into where bottlenecks and workflow disruptions occur.
SAP Signavio can help you with this: the tool scans the entire SAP ECC and SAP S/4 HANA environment, performs comprehensive evaluations, and makes specific recommendations. The next stage is to examine individual processes more closely. For instance, how can you increase the number of order picks without errors? And how can you cut transportation wait times? SAP Signavio can also aid by swiftly detecting and fixing the various bottlenecks. In short, the correct tools enable you to conduct accurate evaluations and make sound decisions.
Process Mining
Many managers make decisions based on intuition and inaccurate or inadequate facts. Process mining gives trustworthy information on the flow of a process. This enables you to implement whole new procedures in detail, rectify inefficiencies, and make smarter judgments. Your happy routes and bottlenecks are clearly visible, making it simple to present and improve complex processes.
- Here are some instances of effective process mining applications:
- Process improvement projects (Lean/Six Sigma)
- Developing business process transformation strategies based on data.
- Business process management involves mapping present processes in preparation for the SAP S/4HANA transformation.
- Measuring process compliance following the SAP S/4HANA transformation.
- Creating audit trails and analyzing audit risks
- Continuous process monitoring in the process industry.
- Understanding the factors that drive KPI performance.
SAP Signavio pulls data from your source systems (such as ERP, WMS, CRM) and loads it into Signavio. The data is reviewed, cleansed, and transformed into a real-time process flow specific to your firm. The program examines the ideal process flow (happy flow) while evaluating any bottlenecks and inefficiencies that depart from the norm. Above all, SAP Signavio also shows how to improve processes and avoid such bottlenecks. Clear dashboards allow you to make improvements based on actual data.
Process mining or process intelligence?
Both technologies enable managers to make educated judgments. However, the decision is based on the specific circumstances. Process Intelligence might signal something is amiss, whereas process mining explains why. So, while Process Intelligence monitors and reports, Process Mining visualizes. In short, you cannot substitute one tool with another. They can, however, wonderfully complement one another.
SAP Signavio & Robosoft
SAP acquired Signavio and integrated it with their platform to model, optimize, and manage business processes. Robosoft, an established SAP partner, focuses on using SAP Signavio to gain a competitive advantage. We are part of the multi-billion-dollar Technopro group and have over 10 years of expertise in providing SAP services such as advisory and business consulting, implementation, and support.
From Consulting and Business Advisory to seamless SAP Signavio Implementation—our vision is to make businesses more agile, lean, and customer-responsive for a superior customer experience that will ensure their acquisition, retention, and re-engagement. Our SAP Signavio-specific capabilities include:
- Consulting & Business Advisory
Assessment of existing processes, change management, scoping, and goal definition. - SAP Signavio Implementation & Transformation
Implementation of process improvement from planning and configuration to testing and deployment
End-to-end process management solutions with SAP Signavio
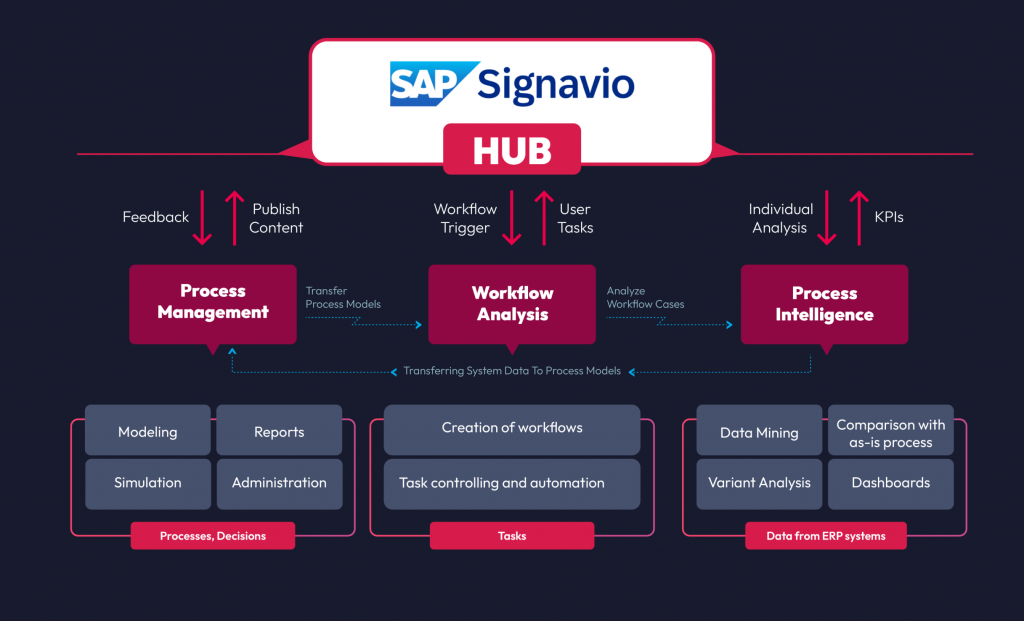
We provide comprehensive SAP Signavio solutions, from setup and enablement to adopting the BPM best practices and ongoing evolution, to meet ever-evolving customer needs while broadening the addressable market. We assist across all core modules of SAP Signavio Process Collaboration Hub.



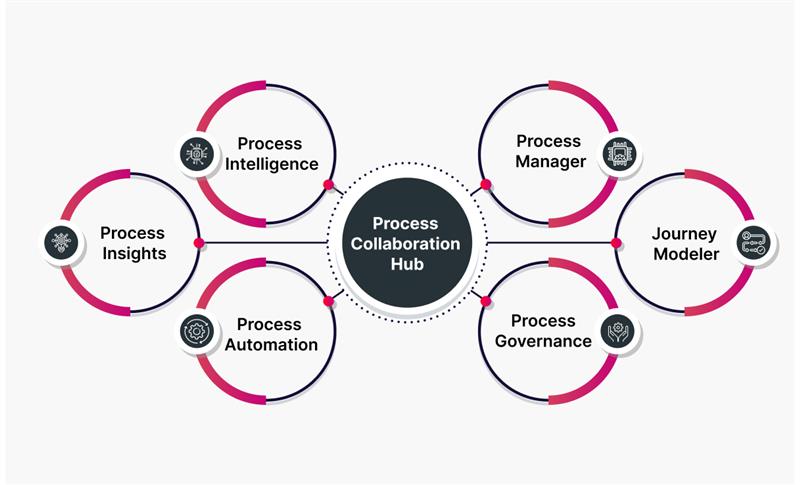
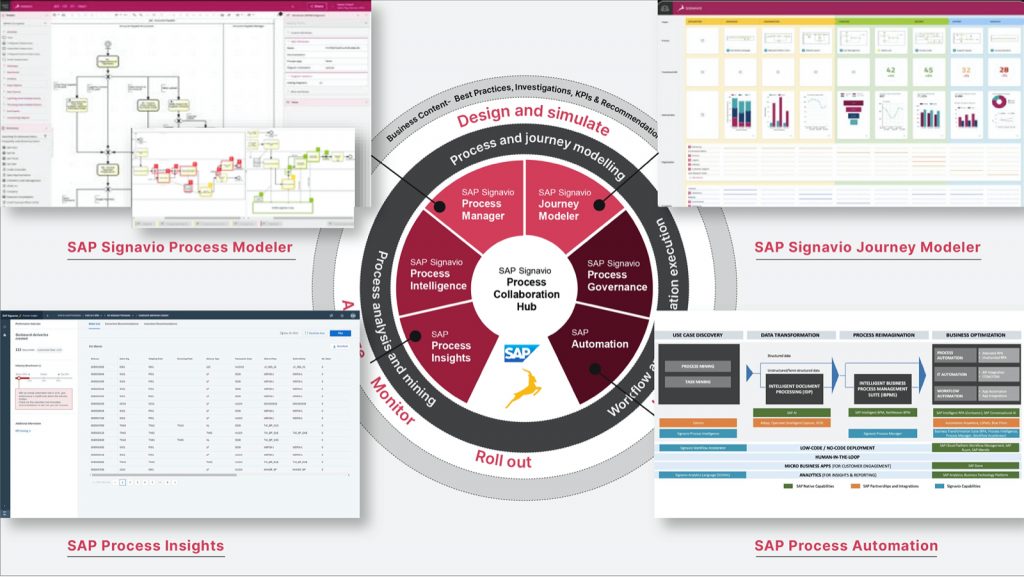

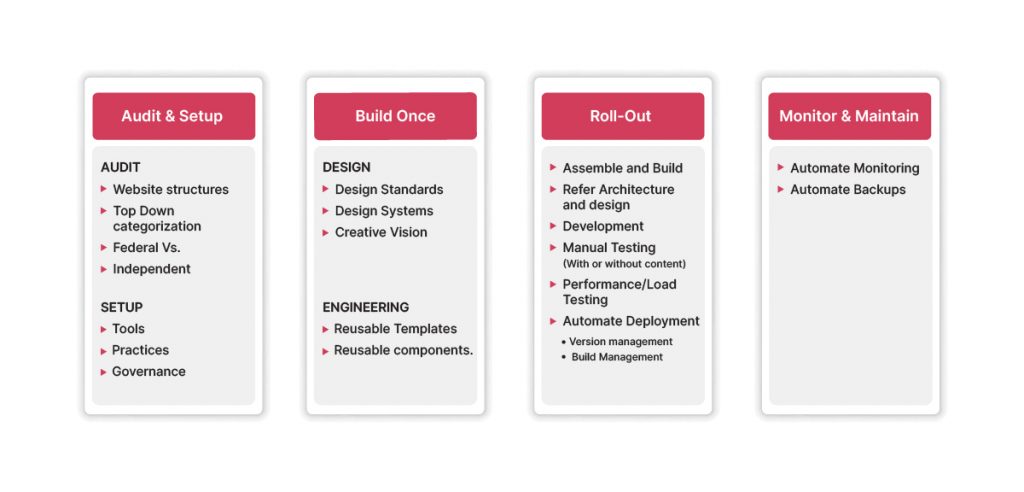 Step 1: Audit and plan based on strategy, design, and technology
Step 1: Audit and plan based on strategy, design, and technology