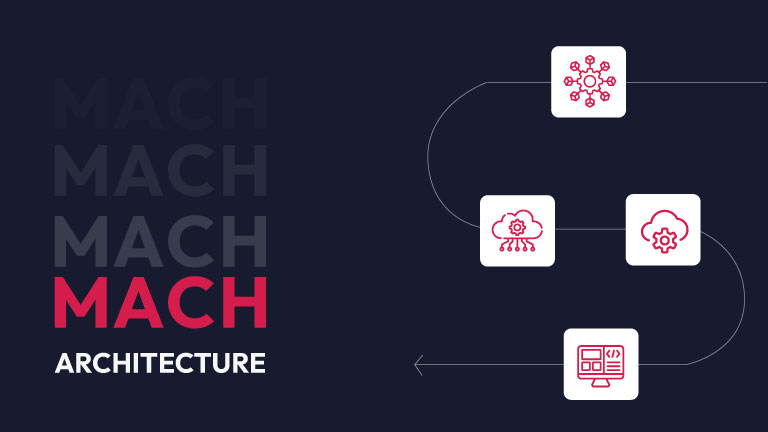
MACH architecture offers a framework for building adaptable digital solutions. It promotes a modular approach, using best-of-breed services and technologies to solve business challenges. MACH (Microservices, API-first, Cloud-native, and Headless) empowers organizations to create flexible, future-proof systems by enabling the composition of pluggable, scalable, and independently deployable components. This architecture is essential for businesses seeking to rapidly innovate and deliver exceptional user experiences in today’s dynamic digital landscape. Let’s look at some aspects of the MACH architecture:
Microservices:
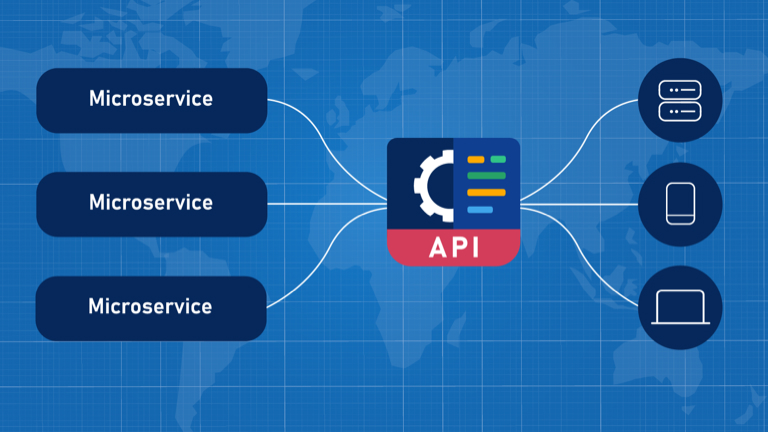
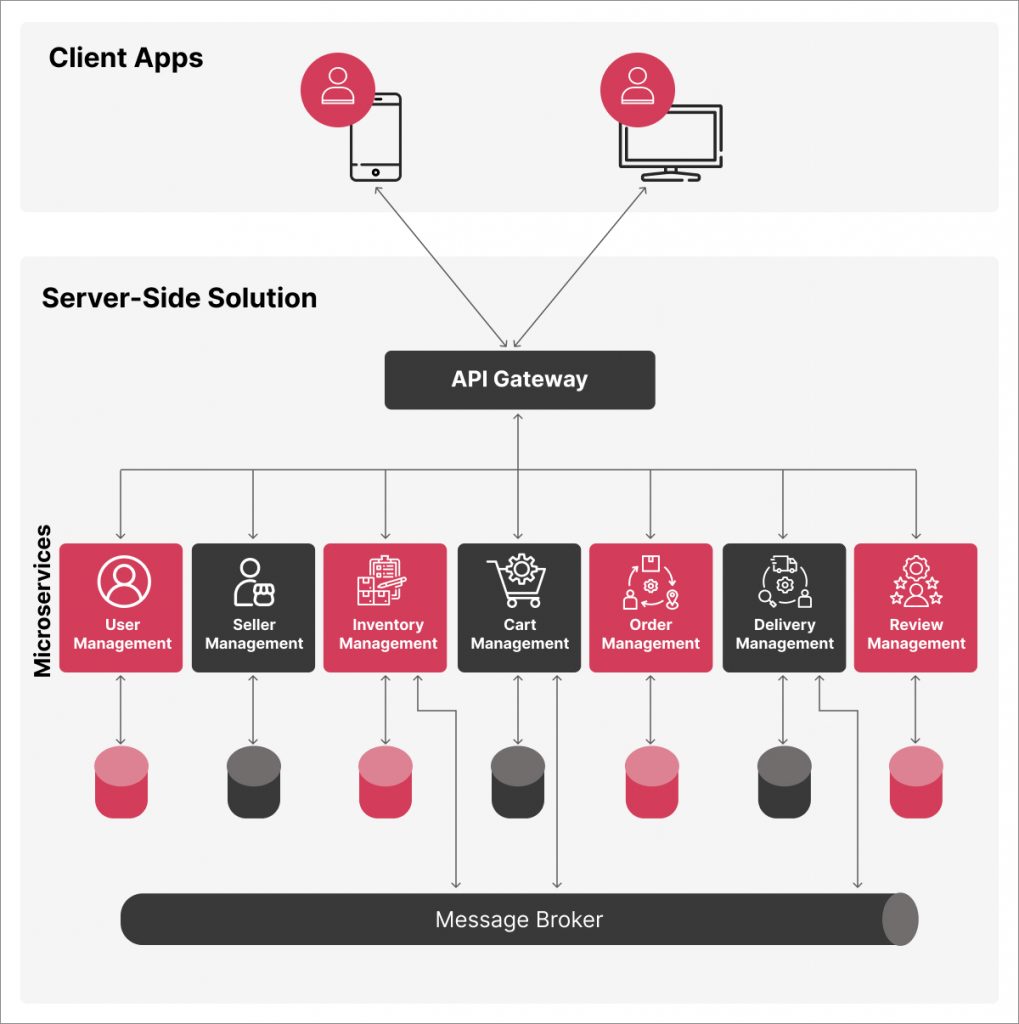
Microservices within MACH architecture break down applications into independently deployable, small services. Each service focuses on a specific business capability and communicates using lightweight APIs. This approach fosters flexibility and rapid development, essential for today’s dynamic digital landscape.
API-first:
An API-first approach prioritizes APIs as the foundation for building applications and services. By developing APIs initially, organizations ensure all functionalities are accessible through standardized interfaces. This promotes integration, flexibility, and streamlined front-end development.
Cloud-native:
Cloud-native applications are designed to fully leverage cloud computing capabilities. By utilizing cloud infrastructure, these applications achieve scalability, resilience, and flexibility. Unlike traditional applications, they can adapt to changing demands and ensure high availability.
Headless:
Headless architecture decouples a web application’s front-end/mobile app from its back-end. This enables independent development and management of the user interface and data storage layers. APIs deliver content, products, or services to any device, while content creators focus on content management without UI constraints.
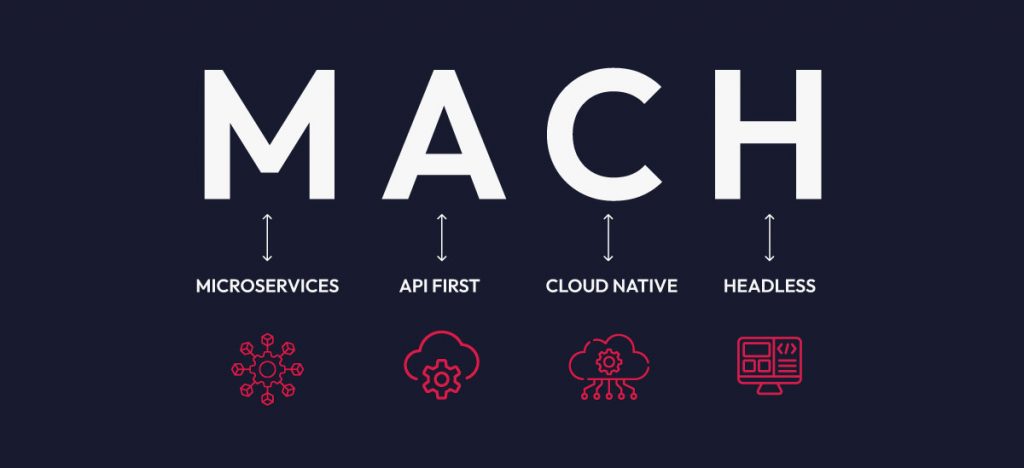
MACH architecture: driving digital transformation
MACH architecture is a cornerstone of modern software development. Its emphasis on agility, scalability, and flexibility aligns perfectly with today’s fast-paced digital landscape. By shifting from monolithic systems to composable architectures, MACH empowers businesses to innovate rapidly and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
- Catalyst for market speed and agility: MACH architecture empowers businesses to match the market’s rapid pace and adaptability. This is achieved through accelerated development and deployment, as well as flexible scaling. Microservices, the foundation of MACH architecture, streamline development by breaking down applications into smaller, independent components. This modular approach expedites updates and improvements, enabling faster response to market shifts and customer demands. Cloud-native design is the other key element. It provides the agility to scale resources up or down in response to real-time needs. This dynamic approach optimizes costs while maintaining performance.
- Enhances customer experience: MACH architecture significantly enhances customer experience through personalized and seamless digital interactions. The headless component empowers businesses to deliver tailored content across various platforms and devices, creating highly personalized experiences. By decoupling front-end and back-end, MACH offers unparalleled content flexibility. The API-first approach fosters seamless integration of functionalities, resulting in a cohesive and engaging user journey. This enables richer feature sets and smoother interactions.
- Future-proofing and continuous innovation: MACH architecture positions businesses for long-term success by enabling future-proofing and continuous innovation. Its modular structure facilitates seamless integration of emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and machine learning. This adaptability accelerates innovation and market entry for new solutions and services. Beyond agility, MACH offers sustainable scalability. Businesses can expand operations without compromising performance or efficiency. This ensures long-term growth and operational viability.
- Enhances reliability and security: MACH architecture significantly improves system reliability and security compared to traditional architectures. The microservices approach isolates issues, preventing system-wide failures. This ensures continuous operation and service delivery. The API-first design provides granular security control through controlled access points. This reduces vulnerabilities and strengthens overall system security.
- Drives economic efficiency: MACH architecture optimizes economic efficiency through cost-effective scaling and resource utilization. Cloud-native infrastructure enables pay-as-you-go pricing, aligning resource consumption with actual demand. This reduces costs and promotes scalability without compromising performance. Microservices and API-first approaches further enhance efficiency by optimizing resource allocation, simplifying updates, and streamlining processes.
By combining agility, adaptability, and economic efficiency, MACH architecture empowers businesses to implement advanced digital solutions while effectively managing financial resources and operational costs.
Real-life examples of MACH architecture
- Contentful: A cloud-native content management system that uses a Headless architecture to deliver content across multiple channels and devices. It is API-first, enabling developers to create custom content models and integrate with other systems and services efficiently.
- Shopify: A cloud-based e-commerce platform employing a Headless architecture, allowing developers to create custom storefronts and shopping experiences. As an API-first platform, Shopify facilitates easy integration with other systems and services.
- Moltin: A cloud-native e-commerce platform built on a Microservices architecture, allowing developers to quickly and easily create custom e-commerce experiences. It is also API-first, simplifying integration with other systems and services.
- Algolia: A cloud-native search-as-a-service platform using a Microservices architecture to provide fast and flexible search experiences. Like the others, Algolia is API-first, allowing seamless integration with other systems and services.
These examples illustrate how MACH architecture can create flexible, scalable, and personalized digital experiences across various industries and use cases.
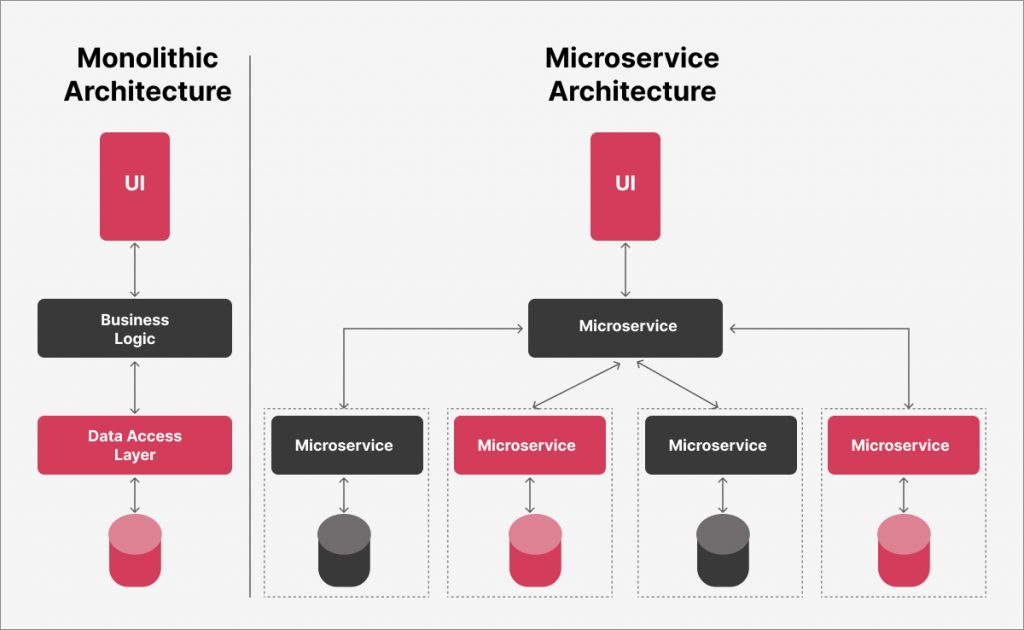
Monolithic architecture vs MACH architecture: A Comparison
Monolithic architecture and MACH architecture represent two distinct approaches to creating digital experiences. Below is a comparison between them:
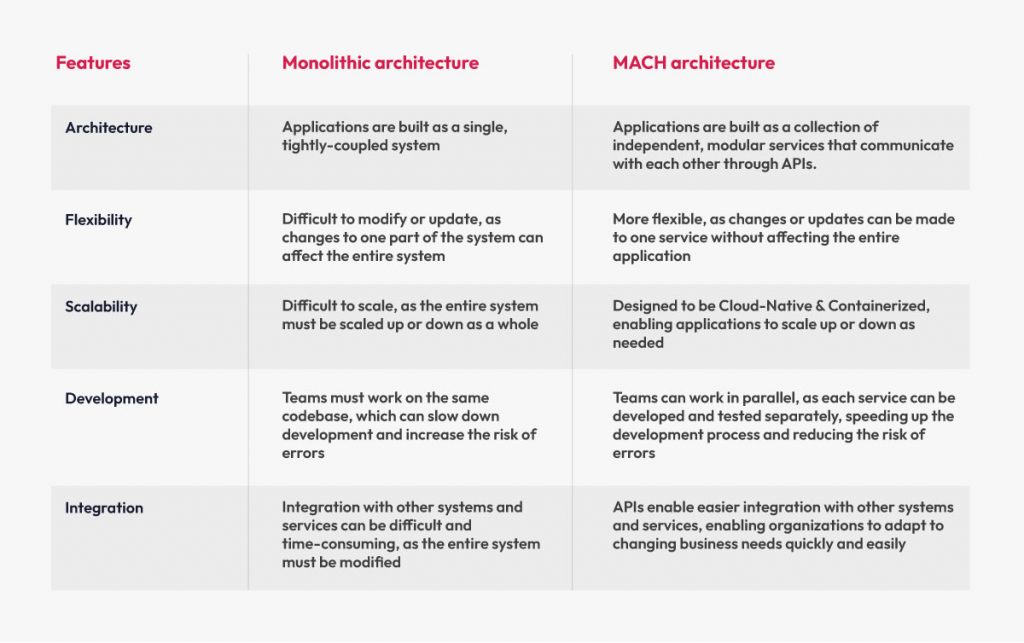
The choice between Monolithic and Microservices should be based on carefully considering the specific requirements and trade-offs of the project at hand.
Evaluating MACH architecture
Determining if MACH architecture suits your digital projects requires considering several factors:
- Business Needs: Assess MACH’s alignment with your organization’s goals, focusing on scalability, flexibility, speed, and personalization.
- Technical Expertise: Evaluate your team’s capabilities or the need for external expertise to implement MACH architecture.
- Integration: Determine MACH’s compatibility with your existing systems and infrastructure, including cloud readiness.
- Cost: Analyze the financial implications of adopting MACH, including infrastructure, tools, and personnel investments.
- User Experience: Assess MACH’s potential to enhance personalization, page load times, and overall customer engagement.
In conclusion, MACH architecture is a transformative approach that empowers organizations to build adaptable, scalable, and customer-centric digital solutions. By embracing microservices, API-first principles, cloud-native technologies, and headless architecture, businesses can unlock new opportunities, accelerate innovation, and deliver exceptional experiences. While the journey to adopting MACH may present challenges, the long-term benefits in terms of agility, efficiency, and competitive advantage are undeniable. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, MACH architecture stands as a robust foundation for future-proof success.