Started in 1934, LEGO was on a growth trajectory for over 50 years. In 1994, owing to the rising popularity of video games and internet the company suffered a major set back and a drop in their sales. In response, they tried diversifying their product portfolio and also collaborated with various production companies to form themed products. While this lead to a short-term rise in numbers the phase ended soon. That is when the organization started with a drastic revamp journey in 2004 with its new strategy called ‘shared vision’. One of the major pillars of this strategy was ‘leveraging digitization’.
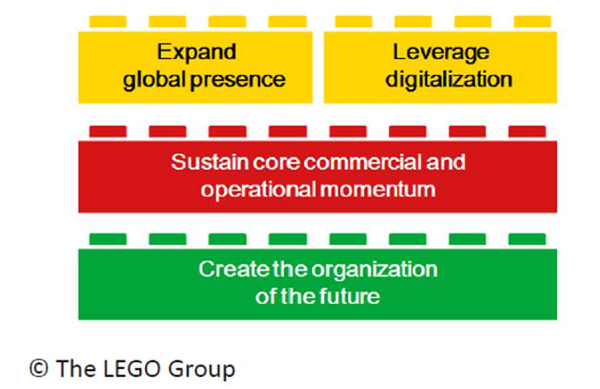
Image Source
Since then, digitization has remained a critical aspect of LEGO’s business strategy. The company has weaved in digital technologies in multiple areas – at a product level, consumer level and at an enterprise level (as depicted in the figure below).
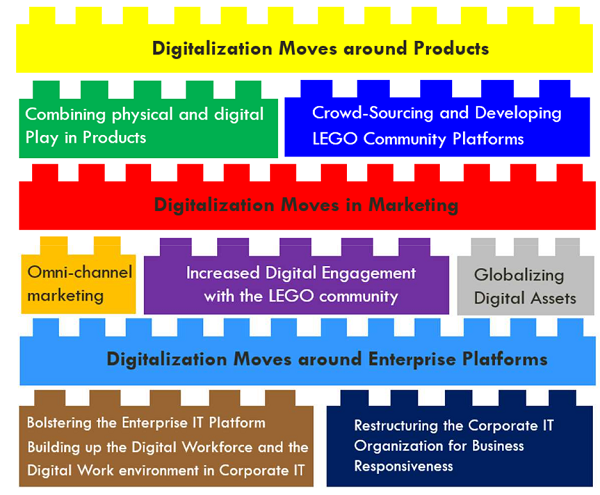
Image Source
All these forces, working together helped LEGO overcome the negative growth in 2003 and mark about 30% growth in the next 10 years, a curve that is on an upward trajectory since.
While LEGO’s success story and digitization efforts sound inspiring and business leaders would love to replicate this success in their respective domains, it is easier said than done. Advancements in technology and digitization are not just changing the way enterprises operate but how various industries operate as a whole. Uber has changed the transportation business, Netflix has completely disrupted the OTT landscape, the automotive industry has recently witnessed the entries of technology companies such as Google, Apple and Microsoft, as vehicles are increasingly getting connected; there a lot of such examples.
As digitization is reshaping the competitive landscape of the companies, it is crucial to understand how short-term are existing business models, in the light of the fast pace of digital disruptions and how they can also leverage technology to address it.
But are enterprises ready for the rapid pace of this change? In this context, digital transformation for enterprises is a must but do organizations really know what does it mean and how to go about it?
As pointed out by this research, while 90% of business leaders deem digital transformation important bit of their business strategy. Almost a similar percentage aren’t sure how to create a plan that integrates the entire digital ecosystem for their organization seamlessly.
There are various challenges that enterprises today face while developing a digital transformation plan. One of the key challenges is disparate systems. The need of digitization though apparent, the need for an organizational level digitization integrating all the departments is still not established.
Also, the rate at which various departments are embracing digitization is also different. For instance, while customer-facing and IT departments are excelling in their efforts of digitization, HR and other departments are lagging behind. This is leading to a lack of strategic alignment between departments, and finally affecting an organization’s progress towards digital transformation.
As per a study, Only the minority (37%) of business leaders see delivering a seamless experience across digital channels as one of the top three priorities for digital transformation in their organization, but half (50%) see this as a top area for focus when aiming to improve the digital experience for customers.
This non-integrated approach towards digital transformation has also to do with the way digitization has evolved. A digitization pyramid has the below elements (as shown in the image below)
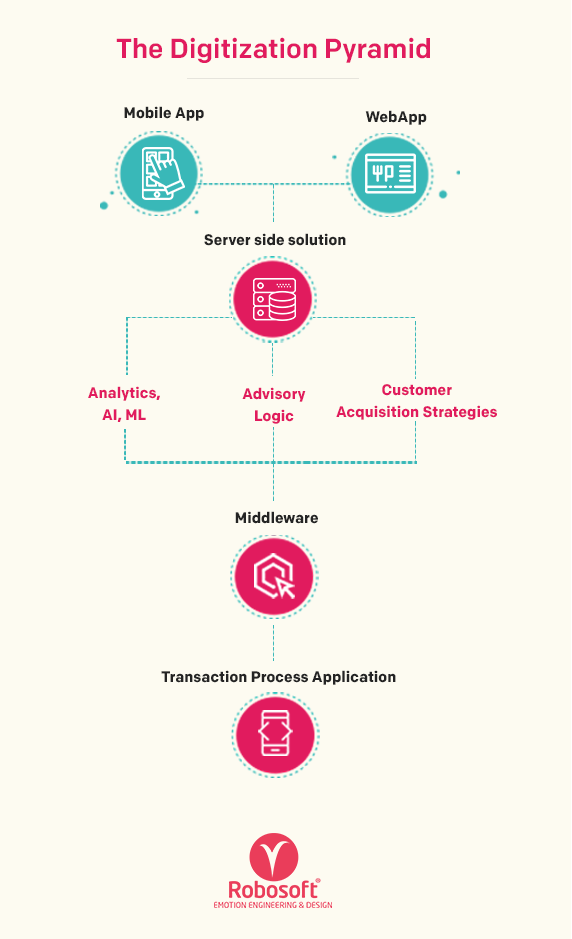
In earlier days, there was a huge emphasis on the lowermost layer which is the Transaction Processing Applications such as SAP, Oracle, Core Banking Solutions, etc. And, as the name suggests that was largely capturing transactions. We went through talking about end-to-end processes, and integrations to avoid Silos.
In the next phase of this evolution we saw a lot of ERP solutions emerging to manage and to some extent centralize data. Today, another layer which is the knowledge-driven or intelligent layer is evolving on top of this, which is enabled with technologies like Analytics, AI, Machine Learning, advisory solutions etc. Further, customer acquisition strategies powered by the data gathered by these solutions are making enterprises understand and design solutions based on consumer insights. Now the same cycle is repeating at a higher level. We are talking about end-to-end solutions, integrations, avoiding silos. But at a higher level of abstraction that focuses on Customer Acquisition strategies, Analytics, ML, AI and so on.
Slowly the Server side is becoming more powerful and prominent. And also the real estate, memory and storage on the Mobile device is increasing. This revolution is what we need to capitalize on. Businesses are adopting enterprise solutions that are solely the Server side solution. At the other end, some talk about only the optimization in the mobile device. However, both these need to function and evolve together to bring about the largest benefit of the current cycle of the digital revolution.
What is an integrated enterprise solution all about?
It is about creating a connected ecosystem where people, businesses and things, are all working together to make business transactions (financial or non-financial) happen.
Take for example – the data recorded by a blood pressure monitoring device remains native to the machine. What if this data can be transferred to a diagnostic centre or a hospital where a physician can access it in real-time and advice the patient on their health, and probably patients can also make payments for the consultation online. This completes a transaction in which a patient, a machine (thing), a platform (cloud computing), one or more applications, businesses and a set of doctors are involved. In this case, technology has enabled the interaction of various components inclusive of the enterprise and the end-user to make a business transaction happen.
There are various technologies that are helping enterprises in developing well-integrated enterprise solutions that act as key enablers for digital business transformation. (As shown in the image below)
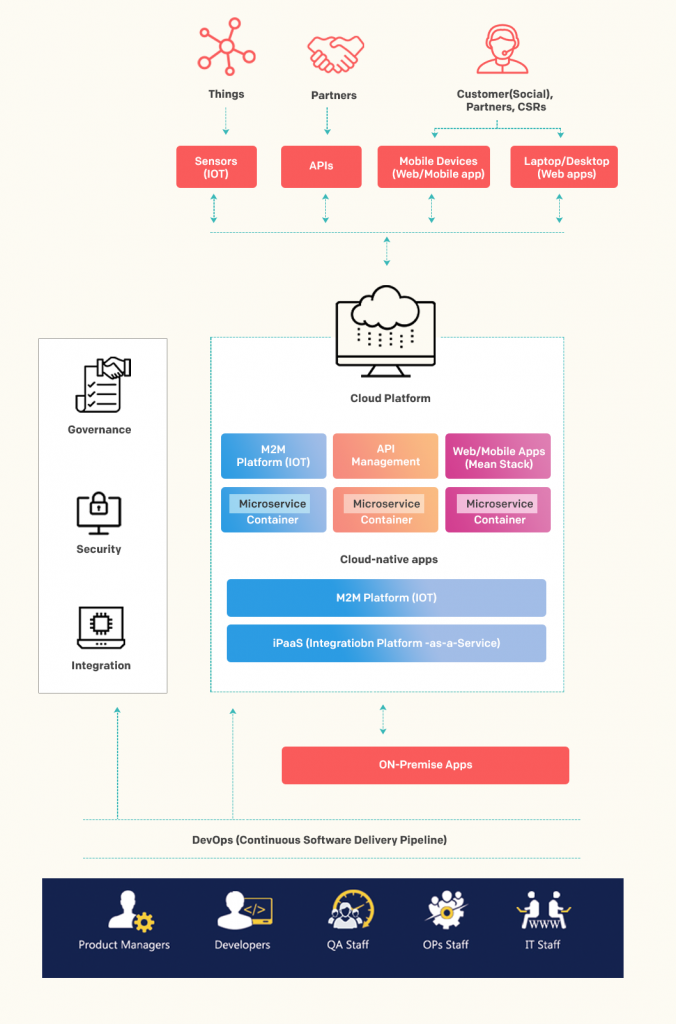
Image Source
1. API Management: APIs are one of the critical aspects of creating a connected enterprise solution. These are the set of functionalities that businesses would share with their partners, customers etc. In this context various API management tools become important. Businesses deploying enterprise solutions for digital transformation would have to look at adopting different aspects of API management. APIs can be used in exposing one or more business services to consumer applications and also help enterprises open data and services that help them integrate with their existing business partners. For example, a manufacturer or retail wholesaler may share its product catalogue and inventory data via API with resellers who want to integrate updated information about available products for sale on their own retail websites.
2. Cloud-Native Apps: When creating a connected enterprise solution there will be a need for more flexible platforms that can enable faster changes in business data and functionality, and cloud-native apps can help businesses achieve that. Cloud-native applications are purpose-built for the cloud model and is a way of approaching the development and deployment of applications in such a way that adapts or understands the various facets and nature of the cloud – resulting in creating processes and workflows that fully take advantage of the platform. In cloud-native apps, these requirements could be easily fulfilled utilizing containers and microservices. With microservices architecture, apps are being built as a distributed collection of services, which pairs up with the distributed nature of the cloud.
3. DevOps: Today, owing to the need of building enterprise solutions that are connected, it is important for businesses to adopt DevOps way of building and delivering software.
According to AWS –
‘’DevOps is the combination of cultural philosophies, practices, and tools that increase an organization’s ability to deliver applications and services at high velocity: evolving and improving products at a faster pace than organizations using traditional software development and infrastructure management processes. This speed enables organizations to better serve their customers and compete more effectively in the market.’’
This helps in creating an ecosystem where various development, operations and in some cases the quality assurance and security teams are merged together for faster delivery of solutions.
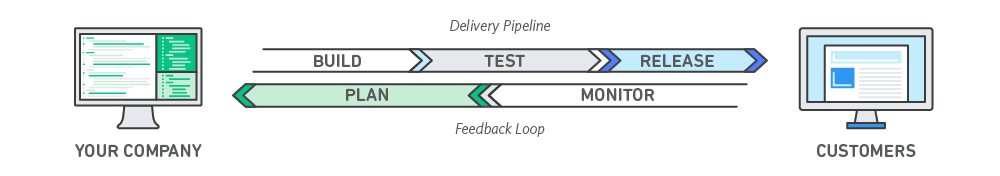
Image Source
4. Internet of Things (IoT): When creating connected enterprise solutions IoT becomes a critical aspect for CIOs and IT leaders. In this context, Machine to Machine platforms (M2M) become the most important part of IoT solutions. Both Machine to Machine and IoT are technologies enabling devices to communicate with each other, M2M refers to isolated instances of device-to-device communication, and IoT refers to a grander scale, synergizing vertical software stacks to automate and manage communications between multiple devices. Bringing these two together will play an important role in created connected enterprise solutions.
5. Analytics: With multiple sources of data from customers, partners, things, customer service representatives etc., it becomes of prime importance for business enterprises to use the data in reshaping their business solutions based on the insights derived from the data and reshaping existing solutions to meet the customer demand. To make the most out of this data Big data technologies and predictive/prescriptive analytics are going to play a decisive role in generating value out of data. Integrating these analytics capabilities with the enterprise solutions is becoming important.
6. Mobility: As smartphones become smarter and more integrated to our lives, business stakeholders internal (employees) and external (customers, vendors, etc.) would want to be connected to businesses through different channels, mobile being one of the most important of these. Enterprises would have to start offering and supporting their products and services across diverse mobile devices and subsequently start strategizing for relevant mobile technology adoption.
7. Web-Scale Technologies: Web-scale technologies refer to an architectural approach which helps in delivering capabilities of large cloud service providers within an enterprise IT setting. Web-scale IT methodology enables businesses in designing, deploying and managing infrastructure at any scale that can be packaged in a number of ways to suit diverse requirements and can scale to any size of business or enterprise. It is not a single technology implementation, but rather a set of capabilities of an overall IT system. Web-scale technologies are redefining the traditional approach towards web/mobile app development enabling digital business transformation.
8. Integration Platform-as-a-Service (iPaaS): While moving applications to the cloud in form of cloud-native apps enables enterprises to develop more agile, faster and flexible solutions, it is not feasible to move all apps into the cloud. Hence it has become essential to integrate cloud-native apps with on-premise apps, this is where iPaaS solutions have become important. These platforms help to integrate develop, execute and govern integration flows between disparate applications. An iPaaS can simplify an organization’s overall system. With the help of a virtual platform, iPaaS connects applications and resources to create a consistent structure. The iPaaS framework creates a seamless integration of resources across multiple clouds and between cloud and legacy applications.
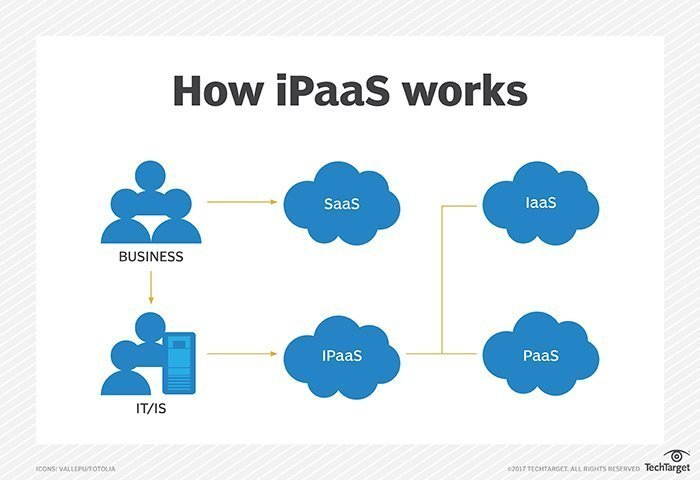
Image Source
In conclusion:
Many organizations today are struggling with digital transformation and facing challenges in their pursuit of building an integrated enterprise solution that gives insight to the end-to-end process. However, with the availability of innovative technologies like SaaS-based digital experience monitoring and analytics, which provide deep, in-depth visibility, unique insights and actionable recommendations this situation is fast changing. In the future we will see an evolution of smarter, intelligent enterprise solutions, that will fuel the digital transformation revolution for enterprises helping them build an integrated ecosystem, benefitting the end user, optimizing workflows and also driving ROI for enterprises.