Over half of the world’s population has access to the internet today. This number will reach 76% by 2030, in which the percentage of people with mobile internet is forecasted to go from 42.4% (2017) to 99.5% by 2030 (a 6.8% CAGR).
Easy access to the internet and higher bandwidths have impacted a lot of facets of our lives. From renting a cab for daily commute to consuming entertainment content to ordering groceries and so on… we get most of these things done online. Food ordering is one such activity which has changed dramatically over the last few years thanks to technology.
According to a Business Insider Intelligence study:
“Orders placed via smartphone are expected to account for more than 10% of all quick-service restaurant sales by 2020, at which point mobile ordering is expected to be a $38 billion industry’’
It is expected that 1.8b new consumers will be added to the world economy by 2025, close to a 25% increase from 2017. Which can result in the addition of another $500b for global restaurants to share, emerging economies will be a major contributor to this growth. In markets like India, food-aggregator apps are even transforming restaurant chains’ view of their own businesses, aside from urban dining habits. A tea retailer in India, Chai Point launched a cafe in Bengaluru with an area demarcated for food-delivery apps’ personnel.
A typical day in a consumer’s life maybe be filled with some or all of these moments, where digital plays a role:
On-the-go food ordering, offers based on past purchases, incentives to increase the order size, cutting down on waiting time at a brick & mortar restaurant, discovering new restaurants, providing feedback on food & service quality, convenience of a appointed-time delivery, notifications to stock up for a big game on TV, ease of ordering through voice-enabled technology and more.
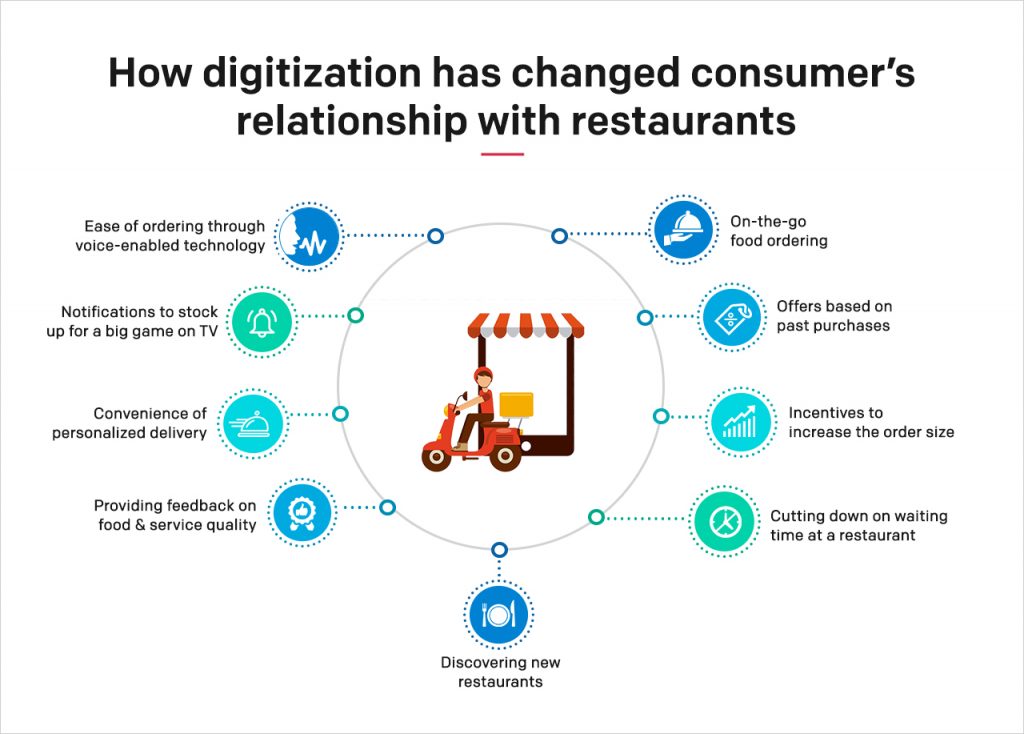
Food aggregator apps like UberEats, GrubHub, Swiggy & Zomato are tapping into the inherent needs of today’s consumers. Convenience, anytime-anywhere delivery, choice and easy payment options are some of the reasons for their success.
The BCG analysis diagram below elaborates the consumer engagement in context to the restaurant brands and their interaction with them.
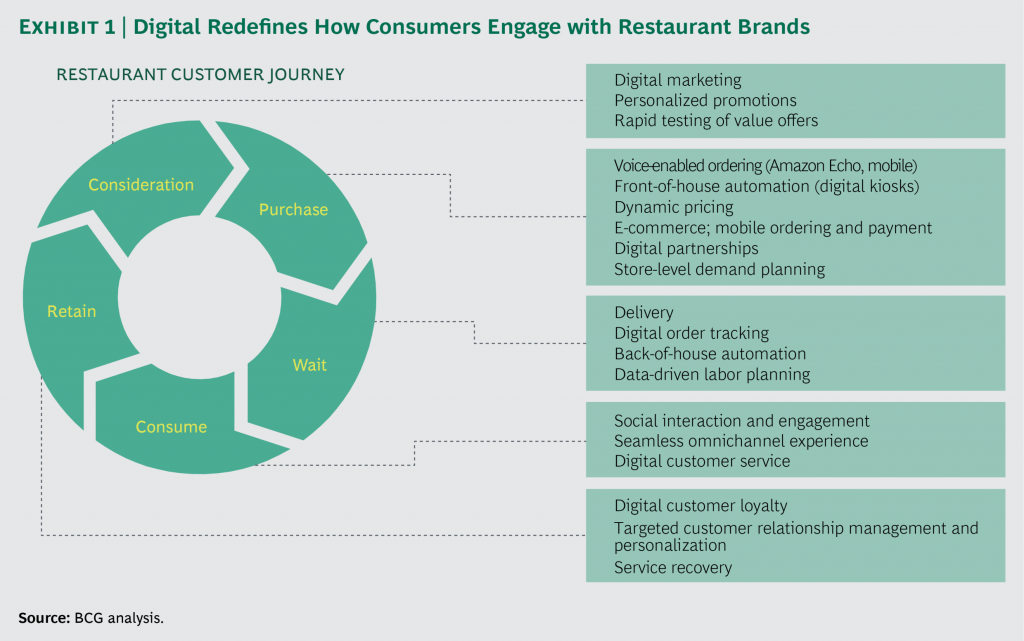
Image Source
The restaurant business has always tapped into the need for convenience and experience of the consumers. Today’s consumers seek newer experiences that are in line with their changing lifestyle. With the advent of the digital medium, the standards of convenience have risen even further. To succeed, food businesses will have to continuously up that standard and make it more and more convenient and easy for the consumers to get food delivered at their doorstep.
To support the discussion here are a few facts from the KPMG report on “An appetite for change” which outline what consumers expect from restaurants and why consumer convenience is important for the future.
- 64% – Consumers who are more adventurous in their restaurant food choices than they were two years ago
- 69% – Consumers who are more likely to visit a restaurant that offers locally produced food items
- 60% – Consumers who are likely to choose a restaurant that offers items grown or raised in an Eco-friendly way
- 76% – Consumers who are more likely to visit a restaurant that offers healthful options
- 79% – Consumers who say restaurant technology increases convenience
- 70% – Smartphone users who view restaurant menus on their phones at least a few times per year
- 32% – Smartphone users who are willing to use an app to pay for meals instead of using cash or card

New-age technologies have made it easier for restaurants to know and cater to the needs of their patrons in innovative ways. With the massive amount of digital footprint that consumers have today, there is more than enough information available about the consumer. The use of Big Data can capture this enormous amount of information starting from consumer behavior to store level data and lay the foundation of personalization, demand forecasting, labour forecasting, order accuracy, etc.
Further technologies based on Artificial Intelligence like chatbots and recommendation engines, etc. can be trained basis this huge amount of data captured and trained to customize user interaction.
Companies are developing unified technology platforms and single Point-of-Sale (PoS) systems to enable consistent data flow to facilitate advanced analytics. At the same time companies are using Application Programming Interfaces (API’s) to facilitate inevitable innovations and integrate third-party platforms (for example, ordering through Amazon Echo or Google Home). On the other side tech players are moving to cloud-based platforms that support real-time data reporting and analytics.
Technology is disrupting the Industry and there are new horizons open for advanced automation, machine learning, and interfaces such as Voice – may sooner or later enter the mainstream.
Companies must adapt to and build capabilities on the digital front or they may miss the bus in such a drastically changing industry. If not now, it’ll be too late for companies to bridge the gap and the competitors will dominate the gameplay.
Consumers have already started blurring the line between online and offline dining decisions, and the ball is in the company’s court to hit it in the right direction or not, in order to win the Consumer Convenience game.





